Page 479 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 479
Pharmacotherapy for Mechanical Ventilation 445
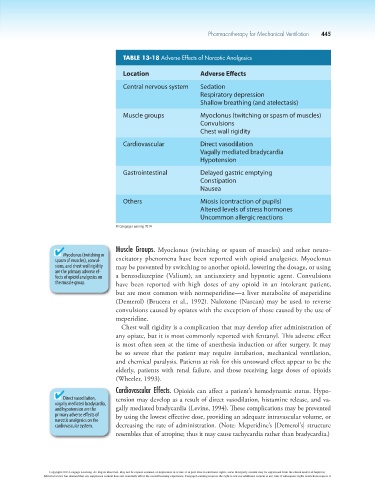
TABLE 13-18 Adverse Effects of Narcotic Analgesics
Location Adverse Effects
Central nervous system Sedation
Respiratory depression
Shallow breathing (and atelectasis)
Muscle groups Myoclonus (twitching or spasm of muscles)
Convulsions
Chest wall rigidity
Cardiovascular Direct vasodilation
Vagally mediated bradycardia
Hypotension
Gastrointestinal Delayed gastric emptying
Constipation
Nausea
Others Miosis (contraction of pupils)
Altered levels of stress hormones
Uncommon allergic reactions
© Cengage Learning 2014
Muscle Groups. Myoclonus (twitching or spasm of muscles) and other neuro-
Myoclonus (twitching or
spasm of muscles), convul- excitatory phenomena have been reported with opioid analgesics. Myoclonus
sions, and chest wall rigidity may be prevented by switching to another opioid, lowering the dosage, or using
are the primary adverse ef-
fects of opioid analgesics on a benzodiazepine (Valium), an antianxiety and hypnotic agent. Convulsions
the muscle group. have been reported with high doses of any opioid in an intolerant patient,
but are most common with normeperidine—a liver metabolite of meperidine
(Demerol) (Brucera et al., 1992). Naloxone (Narcan) may be used to reverse
convulsions caused by opiates with the exception of those caused by the use of
meperidine.
Chest wall rigidity is a complication that may develop after administration of
any opiate, but it is most commonly reported with fentanyl. This adverse effect
is most often seen at the time of anesthesia induction or after surgery. It may
be so severe that the patient may require intubation, mechanical ventilation,
and chemical paralysis. Patients at risk for this untoward effect appear to be the
elderly, patients with renal failure, and those receiving large doses of opioids
(Wheeler, 1993).
Cardiovascular Effects. Opioids can affect a patient’s hemodynamic status. Hypo-
Direct vasodilation, tension may develop as a result of direct vasodilation, histamine release, and va-
vagally mediated bradycardia,
and hypotension are the gally mediated bradycardia (Levine, 1994). These complications may be prevented
primary adverse effects of by using the lowest effective dose, providing an adequate intravascular volume, or
narcotic analgesics on the
cardiovascular system. decreasing the rate of administration. (Note: Meperidine’s [Demerol’s] structure
resembles that of atropine; thus it may cause tachycardia rather than bradycardia.)
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.