Page 509 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 509
Procedures Related to Mechanical Ventilation 475
For patients receiving mechanical ventilation, an adaptor for the bronchoscope
Hypoxia and increase in may be used. Minor air leak may be compensated by increasing the tidal volume.
peak inspiratory pressure are
common when bronchoscopy The pressure limit may need to be increased to make allowance for a larger tidal
is done on patients receiving
mechanical ventilation. volume and insertion tube in the endotracheal tube.
Types of Specimen
In addition to pulmonary secretions, a flexible bronchoscope can collect other special
specimens. Examples of these specimens are biopsy (forceps biopsy, transbronchial
lung biopsy, and transbronchial needle aspiration biopsy) samples and bronchial
brushing samples. Typically, biopsies collect tissue samples for examination, whereas
bronchial brushing with or without alveolar lavage collects samples for cytological
examination (Hattotuwa et al., 2002; Olympus America, Inc. 2003).
Secretion Collection. Pulmonary secretions are sometimes required for microscopic,
culture and sensitivity, or cytology studies. These secretions are suctioned with a
vacuum source and collected in a sterile sputum specimen trap. If the secretions are
thick, pulmonary lavage with a saline solution may be necessary.
Forceps Biopsy. Forceps biopsy is done within the visual range of the bronchoscope.
forceps biopsy: Tissue specimens
collected by the forceps located Tissue specimens are obtained by passing the biopsy forceps through the biopsy channel
at the distal end of the insertion outlet (Figure 14-10A). The razor-sharp biopsy device at the distal end of the forceps can
tube.
be opened and closed by the operator using the control handle. The tissue specimen col-
lected by the forceps is retrieved and put in a formalin solution for laboratory analysis.
Transbronchial Lung Biopsy. Transbronchial lung biopsy (TBLB) is sometimes neces-
transbronchial lung biopsy
(TBLB): Tissue specimens col- sary to obtain a definitive diagnosis based on preliminary radiographic findings. Lung
lected by the forceps during a specimens are obtained by using a similar approach as in forceps biopsy. The patient is
forced exhalation maneuver.
asked to inhale maximally, and the opened forceps are advanced deep into the distal
airway near the target site. The patient then exhales maximally causing compression
of the lung tissue around the biopsy forceps. The opened forceps are then closed by
force. After removal of the forceps, the specimen is retrieved for laboratory analysis.
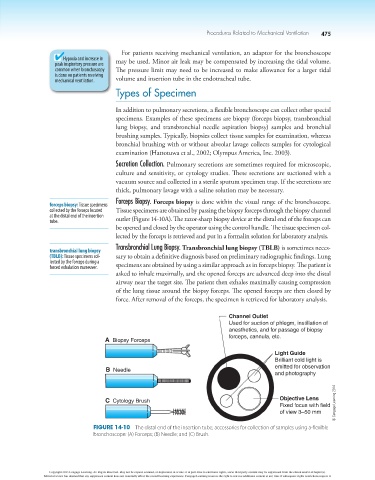
Channel Outlet
Used for suction of phlegm, instillation of
anesthetics, and for passage of biopsy
forceps, cannula, etc.
A Biopsy Forceps
Light Guide
Brilliant cold light is
emitted for observation
B Needle
and photography
C Cytology Brush Objective Lens
Fixed focus with field © Cengage Learning 2014
of view 3–50 mm
Figure 14-10 The distal end of the insertion tube; accessories for collection of samples using a-flexible
bronchoscope: (A) Forceps; (B) Needle; and (C) Brush.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.