Page 505 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 505
Procedures Related to Mechanical Ventilation 471
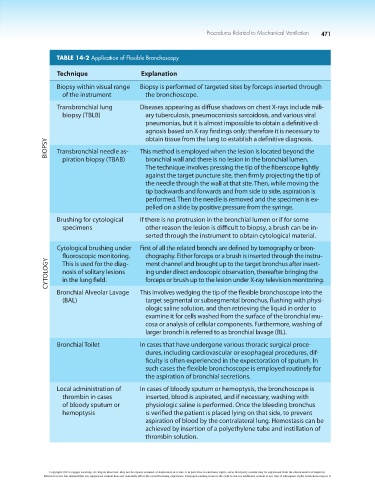
TABLE 14-2 Application of Flexible Bronchoscopy
Technique Explanation
Biopsy within visual range Biopsy is performed of targeted sites by forceps inserted through
of the instrument the bronchoscope.
Transbronchial lung Diseases appearing as diffuse shadows on chest X-rays include mili-
biopsy (TBLB) ary tuberculosis, pneumoconiosis sarcoidosis, and various viral
pneumonias, but it is almost impossible to obtain a definitive di-
agnosis based on X-ray findings only; therefore it is necessary to
obtain tissue from the lung to establish a definitive diagnosis.
BIOPSY Transbronchial needle as- This method is employed when the lesion is located beyond the
piration biopsy (TBAB) bronchial wall and there is no lesion in the bronchial lumen.
The technique involves pressing the tip of the fiberscope lightly
against the target puncture site, then firmly projecting the tip of
the needle through the wall at that site. Then, while moving the
tip backwards and forwards and from side to side, aspiration is
performed. Then the needle is removed and the specimen is ex-
pelled on a slide by positive pressure from the syringe.
Brushing for cytological If there is no protrusion in the bronchial lumen or if for some
specimens other reason the lesion is difficult to biopsy, a brush can be in-
serted through the instrument to obtain cytological material.
Cytological brushing under First of all the related bronchi are defined by tomography or bron-
fluoroscopic monitoring. chography. Either forceps or a brush is inserted through the instru-
CYTOLOGY nosis of solitary lesions ing under direct endoscopic observation, thereafter bringing the
ment channel and brought up to the target bronchus after insert-
This is used for the diag-
forceps or brush up to the lesion under X-ray television monitoring.
in the lung field.
Bronchial Alveolar Lavage This involves wedging the tip of the flexible bronchoscope into the
(BAL) target segmental or subsegmental bronchus, flushing with physi-
ologic saline solution, and then retrieving the liquid in order to
examine it for cells washed from the surface of the bronchial mu-
cosa or analysis of cellular components. Furthermore, washing of
larger bronchi is referred to as bronchial lavage (BL).
Bronchial Toilet In cases that have undergone various thoracic surgical proce-
dures, including cardiovascular or esophageal procedures, dif-
ficulty is often experienced in the expectoration of sputum. In
such cases the flexible bronchoscope is employed routinely for
the aspiration of bronchial secretions.
Local administration of In cases of bloody sputum or hemoptysis, the bronchoscope is
thrombin in cases inserted, blood is aspirated, and if necessary, washing with
of bloody sputum or physiologic saline is performed. Once the bleeding bronchus
hemoptysis is verified the patient is placed lying on that side, to prevent
aspiration of blood by the contralateral lung. Hemostasis can be
achieved by insertion of a polyethylene tube and instillation of
thrombin solution.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.