Page 562 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 562
528 Chapter 16
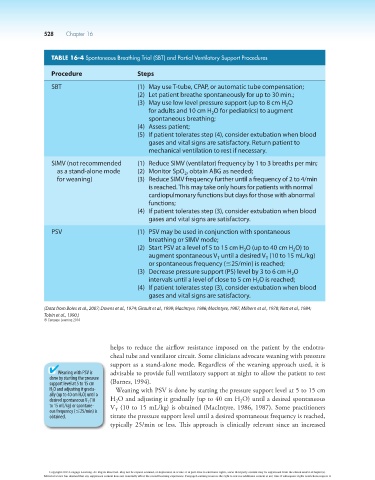
TABLE 16-4 Spontaneous Breathing Trial (SBT) and Partial Ventilatory Support Procedures
Procedure Steps
SBT (1) May use T-tube, CPAP, or automatic tube compensation;
(2) Let patient breathe spontaneously for up to 30 min.;
(3) May use low level pressure support (up to 8 cm H O
2
for adults and 10 cm H O for pediatrics) to augment
2
spontaneous breathing;
(4) Assess patient;
(5) If patient tolerates step (4), consider extubation when blood
gases and vital signs are satisfactory. Return patient to
mechanical ventilation to rest if necessary.
SIMV (not recommended (1) Reduce SIMV (ventilator) frequency by 1 to 3 breaths per min;
as a stand-alone mode (2) Monitor SpO , obtain ABG as needed;
2
for weaning) (3) Reduce SIMV frequency further until a frequency of 2 to 4/min
is reached. This may take only hours for patients with normal
cardiopulmonary functions but days for those with abnormal
functions;
(4) If patient tolerates step (3), consider extubation when blood
gases and vital signs are satisfactory.
PSV (1) PSV may be used in conjunction with spontaneous
breathing or SIMV mode;
(2) Start PSV at a level of 5 to 15 cm H O (up to 40 cm H O) to
2
2
augment spontaneous V until a desired V (10 to 15 mL/kg)
T
T
or spontaneous frequency (#25/min) is reached;
(3) Decrease pressure support (PS) level by 3 to 6 cm H O
2
intervals until a level of close to 5 cm H O is reached;
2
(4) If patient tolerates step (3), consider extubation when blood
gases and vital signs are satisfactory.
(Data from Boles et al., 2007; Downs et al., 1974; Girault et al., 1999; MacIntyre, 1986; MacIntyre, 1987, Milbern et al., 1978; Nett et al., 1984;
Tobin et al., 1990.)
© Cengage Learning 2014
helps to reduce the airflow resistance imposed on the patient by the endotra-
cheal tube and ventilator circuit. Some clinicians advocate weaning with pressure
support as a stand-alone mode. Regardless of the weaning approach used, it is
Weaning with PSV is advisable to provide full ventilatory support at night to allow the patient to rest
done by starting the pressure
support level at 5 to 15 cm (Barnes, 1994).
H 2 O and adjusting it gradu- Weaning with PSV is done by starting the pressure support level at 5 to 15 cm
ally (up to 40 cm H 2 O) until a
desired spontaneous V T (10 H O and adjusting it gradually (up to 40 cm H O) until a desired spontaneous
2
2
to 15 mL/kg) or spontane- V (10 to 15 mL/kg) is obtained (MacIntyre, 1986, 1987). Some practitioners
ous frequency (#25/min) is T
obtained. titrate the pressure support level until a desired spontaneous frequency is reached,
typically 25/min or less. This approach is clinically relevant since an increased
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.