Page 565 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 565
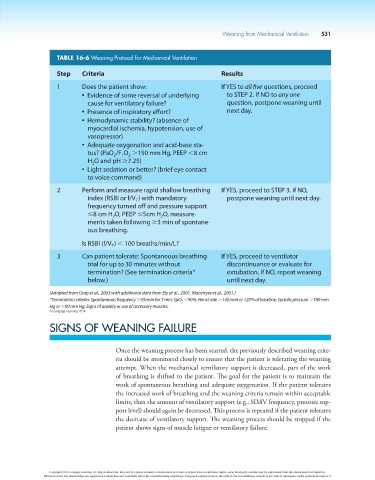
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation 531
TABLE 16-6 Weaning Protocol for Mechanical Ventilation
Step Criteria Results
1 Does the patient show: If YES to all five questions, proceed
Evidence of some reversal of underlying to STEP 2. If NO to any one
cause for ventilatory failure? question, postpone weaning until
Presence of inspiratory effort? next day.
Hemodynamic stability? (absence of
myocardial ischemia, hypotension, use of
vasopressor)
Adequate oxygenation and acid-base sta-
tus? (PaO /F O .150 mm Hg, PEEP ,8 cm
1
2
2
H O and pH $7.25)
2
Light sedation or better? (brief eye contact
to voice command)
2 Perform and measure rapid shallow breathing If YES, proceed to STEP 3. If NO,
index (RSBI or f/V ) with mandatory postpone weaning until next day.
T
frequency turned off and pressure support
#8 cm H O, PEEP #5cm H O, measure-
2
2
ments taken following $3 min of spontane-
ous breathing.
Is RSBI (f/V ) , 100 breaths/min/L?
T
3 Can patient tolerate: Spontaneous breathing If YES, proceed to ventilator
trial for up to 30 minutes without discontinuance or evaluate for
termination? (See termination criteria* extubation. If NO, repeat weaning
below.) until next day.
(Adapted from Grap et al., 2003 with additional data from Ely et al., 2001; MacIntyre et al., 2001.)
*Termination criteria: Spontaneous frequency .35/min for 5 min; SpO 2 ,90%, Heart rate .140/min or 120% of baseline; Systolic pressure .180 mm
Hg or ,90 mm Hg; Signs of anxiety or use of accessory muscles.
© Cengage Learning 2014
SIGNS OF WEANING FAILURE
Once the weaning process has been started, the previously described weaning crite-
ria should be monitored closely to ensure that the patient is tolerating the weaning
attempt. When the mechanical ventilatory support is decreased, part of the work
of breathing is shifted to the patient. The goal for the patient is to maintain the
work of spontaneous breathing and adequate oxygenation. If the patient tolerates
the increased work of breathing and the weaning criteria remain within acceptable
limits, then the amount of ventilatory support (e.g., SIMV frequency, pressure sup-
port level) should again be decreased. This process is repeated if the patient tolerates
the decrease of ventilatory support. The weaning process should be stopped if the
patient shows signs of muscle fatigue or ventilatory failure.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.