Page 633 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 633
Mechanical Ventilation in Nontraditional Settings 599
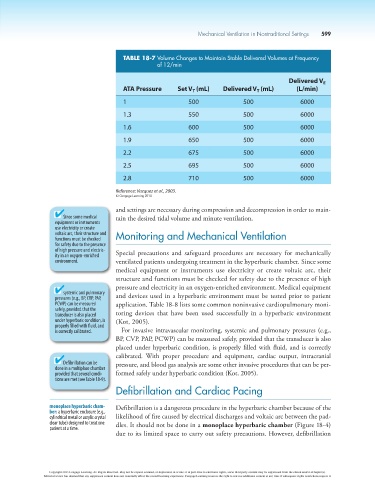
TABLE 18-7 Volume Changes to Maintain Stable Delivered Volumes at Frequency
of 12/min
Delivered V
E
ATA Pressure Set V (mL) Delivered V (mL) (L/min)
T
T
1 500 500 6000
1.3 550 500 6000
1.6 600 500 6000
1.9 650 500 6000
2.2 675 500 6000
2.5 695 500 6000
2.8 710 500 6000
Reference: Vazquez et al., 2003.
© Cengage Learning 2014
and settings are necessary during compression and decompression in order to main-
Since some medical tain the desired tidal volume and minute ventilation.
equipment or instruments
use electricity or create
voltaic arc, their structure and Monitoring and Mechanical Ventilation
functions must be checked
for safety due to the presence
of high pressure and electric- Special precautions and safeguard procedures are necessary for mechanically
ity in an oxygen-enriched
environment. ventilated patients undergoing treatment in the hyperbaric chamber. Since some
medical equipment or instruments use electricity or create voltaic arc, their
structure and functions must be checked for safety due to the presence of high
pressure and electricity in an oxygen-enriched environment. Medical equipment
systemic and pulmonary
pressures (e.g., BP, CVP, PAP, and devices used in a hyperbaric environment must be tested prior to patient
PCWP) can be measured application. Table 18-8 lists some common noninvasive cardiopulmonary moni-
safely, provided that the
transducer is also placed toring devices that have been used successfully in a hyperbaric environment
under hyperbaric condition, is (Kot, 2005).
properly filled with fluid, and
is correctly calibrated. For invasive intravascular monitoring, systemic and pulmonary pressures (e.g.,
BP, CVP, PAP, PCWP) can be measured safely, provided that the transducer is also
placed under hyperbaric condition, is properly filled with fluid, and is correctly
calibrated. With proper procedure and equipment, cardiac output, intracranial
Defibrillation can be pressure, and blood gas analysis are some other invasive procedures that can be per-
done in a multiplace chamber
provided that several condi- formed safely under hyperbaric condition (Kot, 2005).
tions are met (see Table 18-9).
Defibrillation and Cardiac Pacing
monoplace hyperbaric cham- Defibrillation is a dangerous procedure in the hyperbaric chamber because of the
ber: a hyperbaric enclosure (e.g.,
cylindrical metal or acrylic crystal likelihood of fire caused by electrical discharges and voltaic arc between the pad-
clear tube) designed to treat one dles. It should not be done in a monoplace hyperbaric chamber (Figure 18-4)
patient at a time.
due to its limited space to carry out safety precautions. However, defibrillation
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.