Page 634 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 634
600 Chapter 18
TABLE 18-8 Use of Noninvasive Cardiopulmonary Monitoring Devices in a Hyperbaric Chamber
Noninvasive Cardiopulmonary
Monitoring Device Special Consideration
ECG ECG signals are transferred outside the
hyperbaric chamber for monitoring
Pulse oximetry Use is limited to pulse rate only because HBO usually
results in full oxygen saturation for patients without
cardiovascular deficits
Blood pressure Manual method is preferred as automated (electrical)
method may pose fire hazards
Temperature Electrical thermistors should be safe
Mercury-based device should not be used due to
toxicity of mercury under pressure
TcPO and TcPCO Suitable for use in hyperbaric chamber to monitor
2
2
oxygenation and ventilation
P CO 2 Mainstream device may provide false high results due to
ET
increase in gas density
Sidestream device is preferred to monitor end-tidal PCO
2
outside the hyperbaric chamber using decompressed
expiratory tubing
Spirometry and airway pressure Electric spirometer (e.g., Ohmeda 5420) may be used to
monitor airway pressure and exhaled tidal volume
Mechanical respirometer (e.g., Wright) can be used to
monitor exhaled tidal volume
Reference: Kot, 2005.
© Cengage Learning 2014
Courtesy of Environmental Teclonics Corporation
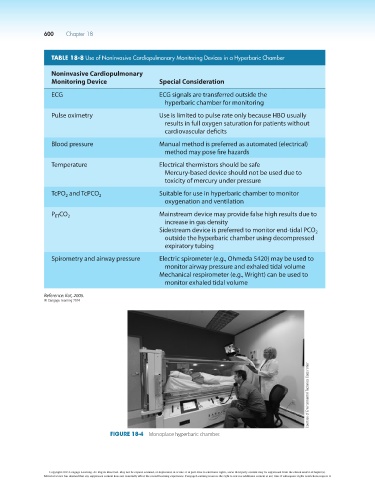
Figure 18-4 Monoplace hyperbaric chamber.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.