Page 92 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 92
58 Chapter 3
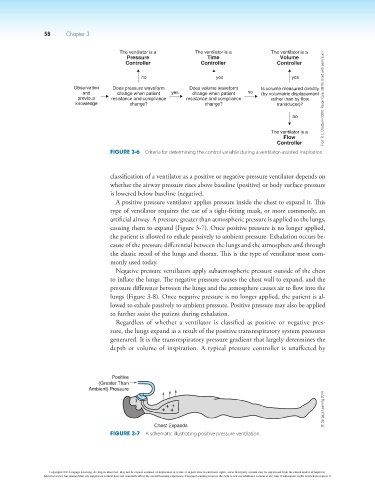
The ventilator is a The ventilator is a The ventilator is a
Pressure Time Volume
Controller Controller Controller
no yes yes
Observation Does pressure waveform Does volume waveform Is volume measured directly
and change when patient yes change when patient no (by volumetric displacement
previous resistance and compliance resistance and compliance rather than by flow From R. L. Chatburn (1991). Respir Care, 36(10). Used with permission.
knowledge change? change? transducer)?
no
The ventilator is a
Flow
Controller
Figure 3-6 Criteria for determining the control variable during a ventilator-assisted inspiration.
classification of a ventilator as a positive or negative pressure ventilator depends on
whether the airway pressure rises above baseline (positive) or body surface pressure
is lowered below baseline (negative).
A positive pressure ventilator applies pressure inside the chest to expand it. This
type of ventilator requires the use of a tight-fitting mask, or more commonly, an
artificial airway. A pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is applied to the lungs,
causing them to expand (Figure 3-7). Once positive pressure is no longer applied,
the patient is allowed to exhale passively to ambient pressure. Exhalation occurs be-
cause of the pressure differential between the lungs and the atmosphere and through
the elastic recoil of the lungs and thorax. This is the type of ventilator most com-
monly used today.
Negative pressure ventilators apply subatmospheric pressure outside of the chest
to inflate the lungs. The negative pressure causes the chest wall to expand, and the
pressure difference between the lungs and the atmosphere causes air to flow into the
lungs (Figure 3-8). Once negative pressure is no longer applied, the patient is al-
lowed to exhale passively to ambient pressure. Positive pressure may also be applied
to further assist the patient during exhalation.
Regardless of whether a ventilator is classified as positive or negative pres-
sure, the lungs expand as a result of the positive transrespiratory system pressures
generated. It is the transrespiratory pressure gradient that largely determines the
depth or volume of inspiration. A typical pressure controller is unaffected by
Positive
(Greater Than
Ambient) Pressure
© Cengage Learning 2014
Chest Expands
Figure 3-7 A schematic illustrating positive pressure ventilation.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.