Page 97 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 97
Classification of Mechanical Ventilators 63
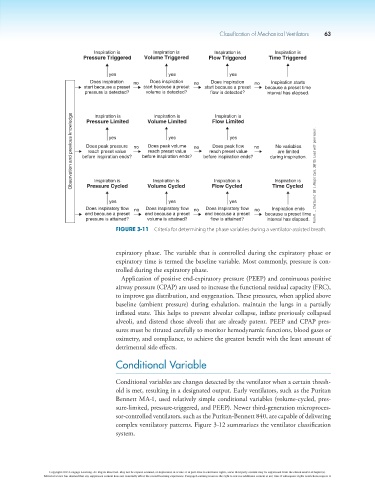
Inspiration is Inspiration is Inspiration is Inspiration is
Pressure Triggered Volume Triggered Flow Triggered Time Triggered
yes yes yes
Does inspiration no Does inspiration no Does inspiration no Inspiration starts
start because a preset start because a preset start because a preset because a preset time
pressure is detected? volume is detected? flow is detected? interval has elapsed.
Observation and previous knowledge before inspiration ends? no before inspiration ends? no before inspiration ends? no during inspiration. From R. L. Chatburn (1991). Respir Care, 36 (10). Used with permission.
Inspiration is
Inspiration is
Inspiration is
Flow Limited
Volume Limited
Pressure Limited
yes
yes
yes
Does peak volume
Does peak pressure
Does peak flow
No variables
reach preset value
reach preset value
reach preset value
are limited
Inspiration is
Inspiration is
Inspiration is
Inspiration is
Pressure Cycled
yes
yes
yes Volume Cycled Flow Cycled Time Cycled
Does inspiratory flow no Does inspiratory flow no Does inspiratory flow no Inspiration ends
end because a preset end because a preset end because a preset because a preset time
pressure is attained? volume is attained? flow is attained? interval has elapsed.
Figure 3-11 Criteria for determining the phase variables during a ventilator-assisted breath.
expiratory phase. The variable that is controlled during the expiratory phase or
expiratory time is termed the baseline variable. Most commonly, pressure is con-
trolled during the expiratory phase.
Application of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) and continuous positive
airway pressure (CPAP) are used to increase the functional residual capacity (FRC),
to improve gas distribution, and oxygenation. These pressures, when applied above
baseline (ambient pressure) during exhalation, maintain the lungs in a partially
inflated state. This helps to prevent alveolar collapse, inflate previously collapsed
alveoli, and distend those alveoli that are already patent. PEEP and CPAP pres-
sures must be titrated carefully to monitor hemodynamic functions, blood gases or
oximetry, and compliance, to achieve the greatest benefit with the least amount of
detrimental side effects.
Conditional Variable
Conditional variables are changes detected by the ventilator when a certain thresh-
old is met, resulting in a designated output. Early ventilators, such as the Puritan
Bennett MA-1, used relatively simple conditional variables (volume-cycled, pres-
sure-limited, pressure-triggered, and PEEP). Newer third-generation microproces-
sor-controlled ventilators, such as the Puritan-Bennett 840, are capable of delivering
complex ventilatory patterns. Figure 3-12 summarizes the ventilator classification
system.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.