Page 426 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 426
/09
/30
P
:57
6
0-4
p40
qxd
19.
pta
2 A
Inc
ra
40
P
M
a
a
K34
0-c
18_
LWB K34 0-c 18_ p40 0-4 19. qxd 6 /30 /09 7 7 :57 P M P a g g e e 40 2 A pta ra Inc . .
LWB
LWBK340-c18_p400-419.qxd 6/30/09 7:57 PM Page 402 Aptara Inc.
402 P A R T III / Assessment of Heart Disease
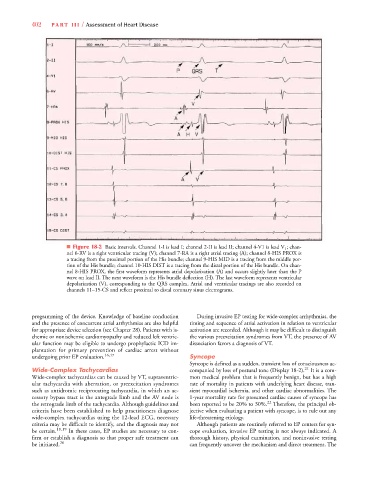
■ Figure 18-2 Basic intervals. Channel 1-I is lead I; channel 2-II is lead II; channel 4-V1 is lead V 1 ; chan-
nel 6-RV is a right ventricular tracing (V); channel 7-RA is a right atrial tracing (A); channel 8-HIS PROX is
a tracing from the proximal portion of the His bundle; channel 9-HIS MID is a tracing from the middle por-
tion of the His bundle; channel 10-HIS DIST is a tracing from the distal portion of the His bundle. On chan-
nel 8-HIS PROX, the first waveform represents atrial depolarization (A) and occurs slightly later than the P
wave on lead II. The next waveform is the His bundle deflection (H). The last waveform represents ventricular
depolarization (V), corresponding to the QRS complex. Atrial and ventricular tracings are also recorded on
channels 11–15-CS and reflect proximal to distal coronary sinus electrograms.
programming of the device. Knowledge of baseline conduction During invasive EP testing for wide-complex arrhythmias, the
and the presence of concurrent atrial arrhythmias are also helpful timing and sequence of atrial activation in relation to ventricular
for appropriate device selection (see Chapter 28). Patients with is- activation are recorded. Although it may be difficult to distinguish
chemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy and reduced left ventric- the various preexcitation syndromes from VT, the presence of AV
ular function may be eligible to undergo prophylactic ICD im- dissociation favors a diagnosis of VT.
plantation for primary prevention of cardiac arrest without
undergoing prior EP evaluation. 16,17 Syncope
Syncope is defined as a sudden, transient loss of consciousness ac-
Wide-Complex Tachycardias companied by loss of postural tone (Display 18-2). 21 It is a com-
Wide-complex tachycardias can be caused by VT, supraventric- mon medical problem that is frequently benign, but has a high
ular tachycardia with aberration, or preexcitation syndromes rate of mortality in patients with underlying heart disease, tran-
such as antidromic reciprocating tachycardia, in which an ac- sient myocardial ischemia, and other cardiac abnormalities. The
cessory bypass tract is the antegrade limb and the AV node is 1-year mortality rate for presumed cardiac causes of syncope has
the retrograde limb of the tachycardia. Although guidelines and been reported to be 20% to 30%. 22 Therefore, the principal ob-
criteria have been established to help practitioners diagnose jective when evaluating a patient with syncope, is to rule out any
wide-complex tachycardias using the 12-lead ECG, necessary life-threatening etiology.
criteria may be difficult to identify, and the diagnosis may not Although patients are routinely referred to EP centers for syn-
be certain. 18,19 In these cases, EP studies are necessary to con- cope evaluation, invasive EP testing is not always indicated. A
firm or establish a diagnosis so that proper safe treatment can thorough history, physical examination, and noninvasive testing
be initiated. 20 can frequently uncover the mechanism and direct treatment. The