Page 611 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 611
M
3 P
3 P
M
g
Pa
Pa
1:4
009
6/2
6/2
009
1:4
0
0
p
p
p
t
ara
ara
t
A
e 5
g
g
e 5
A
87
87
0/0
3
3
55
55
q
q
q
xd
5-5
xd
94.
0/0
3
LWBK340-c24_
LWB K34 0-c 24_ p p pp555-594.qxd 30/06/2009 01:43 PM Page 587 Aptara
5-5
24_
94.
0-c
LWB
K34
C HAPTER 24 / Heart Failure and Cardiogenic Shock 587
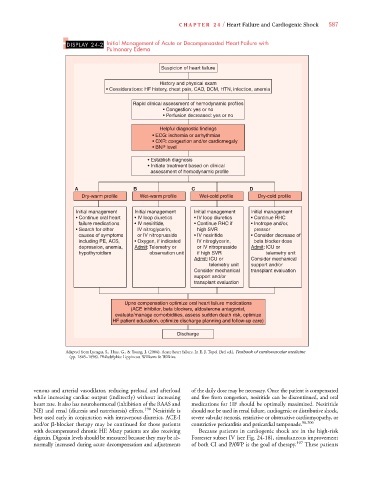
DISPLAY 24-2 Initial Management of Acute or Decompensasted Heart Failure with
Pulmonary Edema
Suspicion of heart failure
History and physical exam
• Considerations: HF history, chest pain, CAD, DCM, HTN, infection, anemia
Rapid clinical assessment of hemodynamic profiles
• Congestion: yes or no
• Perfusion decreased: yes or no
Helpful diagnostic findings
• ECG: ischemia or arrhythmias
• CXR: congestion and/or cardiomegaly
• BNP level
• Establish diagnosis
• Initiate treatment based on clinical
assessment of hemodynamic profile
A B C D
Dry-warm profile Wet-warm profile Wet-cold profile Dry-cold profile
Initial management Initial management Initial management Initial management
• Continue oral heart • IV loop diuretics • IV loop diuretics • Continue RHC
failure medications • IV nesiritide, • Continue RHC if • Inotrope and/or,
• Search for other IV nitroglycerin, high SVR pressor
causes of symptoms or IV nitroprusside • IV nesiritide • Consider decrease of
including PE, ACS, • Oxygen, if indicated IV nitroglycerin, beta blocker dose
depression, anemia, Admit: Telemetry or or IV nitroprusside Admit: ICU or
hypothyroidism observation unit if high SVR telemetry unit
Admit: ICU or Consider mechanical
telemetry unit support and/or
Consider mechanical transplant evaluation
support and/or
transplant evaluation
Upno compensation optimize oral heart failure medications
(ACE inhibitor, beta blockers, aldosterone antagonist,
evaluate/manage comorbidities, assess sudden death risk, optimize
HF patient education, optimize discharge planning and follow-up care)
Discharge
Adapted from Lyengar, S., Hass, G., & Young, J. (2006). Acute heart failure. In E. J. Topol (3rd ed.), Textbook of cardiovascular medicine
(pp. 1845–1898). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
venous and arterial vasodilator, reducing preload and afterload of the daily dose may be necessary. Once the patient is compensated
while increasing cardiac output (indirectly) without increasing and free from congestion, nesiritide can be discontinued, and oral
heart rate. It also has neurohormonal (inhibition of the RAAS and medications for HF should be optimally maximized. Nesiritide
NE) and renal (diuresis and natreiuresis) effects. 190 Nesiritide is should not be used in renal failure, cardiogenic or distributive shock,
best used early in conjunction with intravenous diuretics. ACE-I severe valvular stenosis, restrictive or obstructive cardiomyopathy, or
and/or -blocker therapy may be continued for those patients constrictive pericarditis and pericardial tamponade. 98,206
with decompensated chronic HF. Many patients are also receiving Because patients in cardiogenic shock are in the high-risk
digoxin. Digoxin levels should be measured because they may be ab- Forrester subset IV (see Fig. 24-18), simultaneous improvement
normally increased during acute decompensation and adjustments of both CI and PAWP is the goal of therapy. 197 These patients