Page 854 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 854
LWBK340-c36_p823-841.qxd 29/06/2009 09:01 PM Page 830 Aptara
830 PA R T V / Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
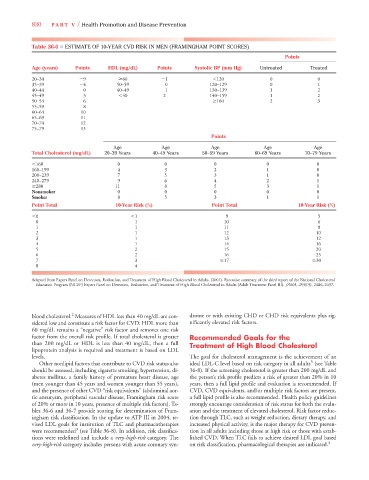
Table 36-6 ■ ESTIMATE OF 10-YEAR CVD RISK IN MEN (FRAMINGHAM POINT SCORES)
Points
Age (years) Points HDL (mg/dL) Points Systolic BP (mm Hg) Untreated Treated
20–34 9 60 1 120 0 0
35–39 4 50–59 0 120–129 0 1
40–44 0 40–49 1 130–139 1 2
45–49 3 40 2 140–159 1 2
50–54 6 160 2 3
55–59 8
60–64 10
65–69 11
70–74 12
75–79 13
Points
Age Age Age Age Age
Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) 20–39 Years 40–49 Years 50–59 Years 60–69 Years 70–79 Years
160 0 0 0 0 0
160–199 4 3 2 1 0
200–239 7 5 3 1 0
240–279 9 6 4 2 1
280 11 8 5 3 1
Nonsmoker 0 0 0 0 0
Smoker 8 5 3 1 1
Point Total 10-Year Risk (%) Point Total 10-Year Risk (%)
0 1 9 5
0 1 10 6
1 1 11 8
2 1 12 10
3 1 13 12
4 1 14 16
5 2 15 20
6 2 16 25
7 3 17 30
8 4
Adapted from Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. (2001). Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol
Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA, 285(19), 2486–2497.
2
blood cholesterol. Measures of HDL less than 40 mg/dL are con- drome or with existing CHD or CHD risk equivalents plus sig-
sidered low and constitute a risk factor for CVD. HDL more than nificantly elevated risk factors.
60 mg/dL remains a “negative” risk factor and removes one risk
factor from the overall risk profile. If total cholesterol is greater Recommended Goals for the
than 200 mg/dL or HDL is less than 40 mg/dL, then a full Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol
lipoprotein analysis is required and treatment is based on LDL
levels. The goal for cholesterol management is the achievement of an
3
Other nonlipid factors that contribute to CVD risk status also ideal LDL-C level based on risk category in all adults (see Table
should be assessed, including cigarette smoking, hypertension, di- 36-8). If the screening cholesterol is greater than 200 mg/dL and
abetes mellitus, a family history of premature heart disease, age the person’s risk profile predicts a risk of greater than 20% in 10
(men younger than 45 years and women younger than 55 years), years, then a full lipid profile and evaluation is recommended. If
and the presence of other CVD “risk equivalents” (abdominal aor- CVD, CVD equivalents, and/or multiple risk factors are present,
tic aneurysm, peripheral vascular disease, Framingham risk score a full lipid profile is also recommended. Health policy guidelines
of 20% or more in 10 years, presence of multiple risk factors). Ta- strongly encourage consideration of risk status for both the evalu-
bles 36-6 and 36-7 provide scoring for determination of Fram- ation and the treatment of elevated cholesterol. Risk factor reduc-
ingham risk classification. In the update to ATP III in 2004, re- tion through TLC, such as weight reduction, dietary therapy, and
vised LDL goals for institution of TLC and pharmacotherapies increased physical activity, is the major therapy for CVD preven-
3
were recommended (see Table 36-8). In addition, risk classifica- tion in all adults including those at high risk or those with estab-
tions were redefined and include a very-high-risk category. The lished CVD. When TLC fails to achieve desired LDL goal based
very-high-risk category includes persons with acute coronary syn- on risk classification, pharmacological therapies are indicated. 3