Page 855 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 855
LWBK340-c36_p823-841.qxd 29/06/2009 09:01 PM Page 831 Aptara
C HAP TE R 36 / Lipid Management and Cardiovascular Disease 831
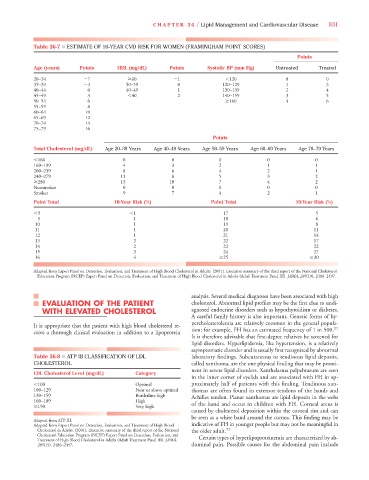
Table 36-7 ■ ESTIMATE OF 10-YEAR CVD RISK FOR WOMEN (FRAMINGHAM POINT SCORES)
Points
Age (years) Points HDL (mg/dL) Points Systolic BP (mm Hg) Untreated Treated
20–34 7 60 1 120 0 0
35–39 3 50–59 0 120–129 1 3
40–44 0 40–49 1 130–139 2 4
45–49 3 40 2 140–159 3 5
50–54 6 160 4 6
55–59 8
60–64 10
65–69 12
70–74 14
75–79 16
Points
Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) Age 20–39 Years Age 40–49 Years Age 50–59 Years Age 60–69 Years Age 70–79 Years
160 0 0 0 0 0
160–199 4 3 2 1 1
200–239 8 6 4 2 1
240–279 11 8 5 3 2
280 13 10 7 4 2
Nonsmoker 0 0 0 0 0
Smoker 9 7 4 2 1
Point Total 10-Year Risk (%) Point Total 10-Year Risk (%)
9 1 17 5
9 1 18 6
10 1 19 8
11 1 20 11
12 1 21 14
13 2 22 17
14 2 23 22
15 3 24 27
16 4 25 30
Adapted from Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. (2001). Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol
Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA, 285(19), 2486–2497.
analysis. Several medical diagnoses have been associated with high
EVALUATION OF THE PATIENT cholesterol. Abnormal lipid profiles may be the first clue to undi-
WITH ELEVATED CHOLESTEROL agnosed endocrine disorders such as hypothyroidism or diabetes.
A careful family history is also important. Genetic forms of hy-
percholesterolemia are relatively common in the general popula-
It is appropriate that the patient with high blood cholesterol re- 21
ceive a thorough clinical evaluation in addition to a lipoprotein tion; for example, FH has an estimated frequency of 1 in 500.
It is therefore advisable that first-degree relatives be screened for
lipid disorders. Hyperlipidemia, like hypertension, is a relatively
asymptomatic disorder and is usually first recognized by abnormal
Table 36-8 ■ ATP III CLASSIFICATION OF LDL laboratory findings. Subcutaneous or tendinous lipid deposits,
CHOLESTEROL called xanthoma, are the one physical finding that may be promi-
nent in severe lipid disorders. Xanthelasma palpebrarum are seen
LDL Cholesterol Level (mg/dL) Category
in the inner corner of eyelids and are associated with FH in ap-
100 Optimal proximately half of patients with this finding. Tendinous xan-
100–129 Near or above optimal thomas are often found in extensor tendons of the hands and
130–159 Borderline high Achilles tendon. Planar xanthomas are lipid deposits in the webs
160–189 High
190 Very high of the hand and occur in children with FH. Corneal arcus is
caused by cholesterol deposition within the corneal rim and can
be seen as a white band around the cornea. This finding may be
Adapted from ATP III.
Adapted from Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood indicative of FH in younger people but may not be meaningful in
Cholesterol in Adults. (2001). Executive summary of the third report of the National the older adult. 22
Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and
Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA, Certain types of hyperlipoproteinemia are characterized by ab-
285(19), 2486–2497. dominal pain. Possible causes for the abdominal pain include