Page 191 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 191
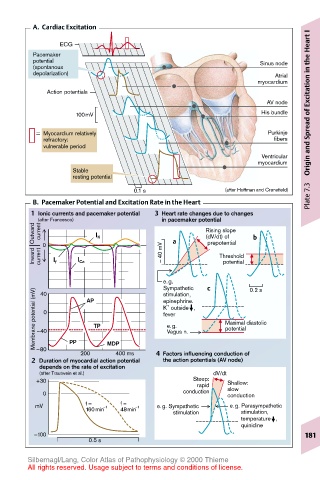
A. Cardiac Excitation
I
Heart
ECG
Pacemaker
potential Sinus node
(spontanous
depolarization) Atrial
myocardium Excitation in the
Action potentials
AV node
100mV His bundle of
Myocardium relatively Purkinje
refractory: fibers
vulnerable period Origin and Spread
Ventricular
myocardium
Stable
resting potential
Plate 7.3
0.1 s (after Hoffman and Cranefield)
B. Pacemaker Potential and Excitation Rate in the Heart
1 Ionic currents and pacemaker potential 3 Heart rate changes due to changes
in pacemaker potential
Outward (after Francesco) I K a Rising slope b
current
(dV/dt) of
prepotential
Inward current 0 I f I Ca – 40 mV Threshold
potential
e.g. c 0.2 s
Sympathetic
Membrane potential (mV) –40 0 AP TP epinephrine. Maximal diastolic
40
stimulation,
+
K outside ,
fever
e.g.
potential
Vagus n.
PP
–80
200 MDP 400 ms 4 Factors influencing conduction of
2 Duration of myocardial action potential the action potentials (AV node)
depends on the rate of excitation
(after Trautwein et al.) dV/dt
+30 Steep: Shallow:
rapid slow
0 conduction conduction
mV f = –1 f = –1 e.g. Sympathetic e.g. Parasympathetic
160min 48min stimulation stimulation,
temperature ,
quinidine
–100 181
0.5 s
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.