Page 23 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 23
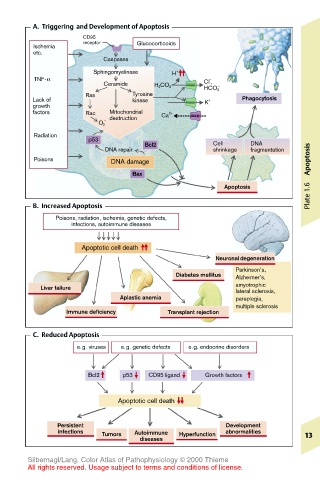
A. Triggering and Development of Apoptosis
CD95
Ischemia receptor Glucocorticoids
etc.
Caspases
Sphingomyelinase H +
TNF-α –
Ceramide Cl ,
H 2 CO 3 –
HCO 3
Ras Tyrosine
Lack of kinase K + Phagocytosis
growth
factors Rac Mitochondrial Ca 2+
– destruction
O 2
Radiation
p53
Bcl2 Cell DNA
DNA repair shrinkage fragmentation
Poisons DNA damage Apoptosis
Bax
Apoptosis
B. Increased Apoptosis Plate 1.6
Poisons, radiation, ischemia, genetic defects,
infections, autoimmune diseases
Apoptotic cell death
Neuronal degeneration
Parkinson’s,
Diabetes mellitus Alzheimer’s,
Liver failure amyotrophic
lateral sclerosis,
Aplastic anemia paraplegia,
multiple sclerosis
Immune deficiency Transplant rejection
C. Reduced Apoptosis
e.g. viruses e.g. genetic defects e.g. endocrine disorders
Bcl2 p53 CD95 ligand Growth factors
Apoptotic cell death
Persistent Development
infections Tumors Autoimmune Hyperfunction abnormalities 13
diseases
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.