Page 171 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 171
148 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
● Many medications administered in critical care affect adverse drug reactions is important in the prevention
sleep architecture. Even vasoactive medications such of escalating sleep disturbances.
as adrenaline have the capacity to affect the quality ● Specific sleep-promoting medications may be admin-
of sleep. Sedatives, especially benzodiazepines and istered once non-pharmacological interventions have
opioids, reduce time in stage 3 and 4 and REM, thus been attempted. Table 7.10 contains a summary of the
reducing the amount and quality of sleep. 153,154 commonly used medications for the general manage-
However pain relief and anxiolysis may be essential ment of insomnia. It should be noted that investiga-
for sleep to occur, but an awareness of potential tions of the effectiveness of these medications have
not been undertaken in the critically ill.
Practice tip
Practice tip
Next time you are at work in ICU take the time to attend to the
noise level. At an appropriate time and position in the ICU close After interviewing the patient or their family about their usual
your eyes for one minute and consider whether you would be sleep and assessing their sleep in ICU you suspect they might
able to rest. In addition find a patient who is well enough to be have an existing untreated sleep disorder. Request the treating
discharged to the hospital ward and ask them about the factors medical team to make a sleep medicine referral. Research indi-
which they found most disruptive to rest and sleep while they cates that untreated sleep problems long-term are associated
were being treated in ICU. with increased risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer.
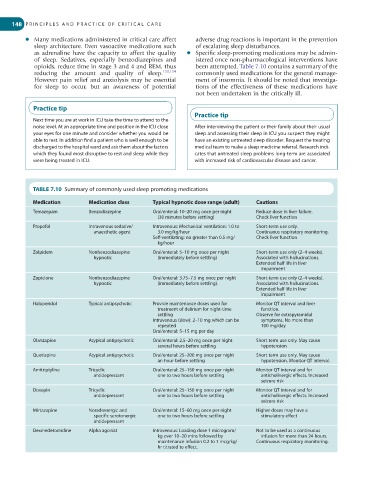
TABLE 7.10 Summary of commonly used sleep promoting medications
Medication Medication class Typical hypnotic dose range (adult) Cautions
Temazepam Benzodiazepine Oral/enteral: 10–20 mg once per night Reduce dose in liver failure.
(30 minutes before settling) Check liver function
Propofol Intravenous sedative/ Intravenous: Mechanical ventilation: 1.0 to Short-term use only.
anaesthetic agent 3.0 mg/kg/hour Continuous respiratory monitoring.
Self-ventilating: no greater than 0.5 mg/ Check liver function
kg/hour
Zolpidem Nonbenzodiazepine Oral/enteral: 5–10 mg once per night Short-term use only (2–4 weeks).
hypnotic (immediately before settling) Associated with hallucinations.
Extended half life in liver
impairment
Zopiclone Nonbenzodiazepine Oral/enteral: 3.75–7.5 mg once per night Short-term use only (2–4 weeks).
hypnotic (immediately before settling). Associated with hallucinations.
Extended half life in liver
impairment
Haloperidol Typical antipsychotic Provide maintenance doses used for Monitor QT interval and liver
treatment of delirium for night-time function.
settling Observe for extrapyramidal
Intravenous (slow): 2–10 mg which can be symptoms. No more than
repeated 100 mg/day
Oral/enteral: 5–15 mg per day
Olanzapine Atypical antipsychotic Oral/enteral: 2.5–20 mg once per night Short term use only. May cause
several hours before settling hypotension
Quetiapine Atypical antipsychotic Oral/enteral: 25–200 mg once per night Short term use only. May cause
an hour before settling hypotension. Monitor QT interval.
Amitriptyline Tricyclic Oral/enteral: 25–150 mg once per night Monitor QT interval and for
antidepressant one to two hours before settling anticholinergic effects. Increased
seizure risk
Doxepin Tricyclic Oral/enteral: 25–150 mg once per night Monitor QT interval and for
antidepressant one to two hours before settling anticholinergic effects. Increased
seizure risk
Mirtazapine Noradrenergic and Oral/enteral: 15–60 mg once per night Higher doses may have a
specific serotonergic one to two hours before settling stimulatory effect
antidepressant
Dexmedetomidine Alpha agonist Intravenous: Loading dose 1 microgram/ Not to be used as a continuous
kg over 10–20 mins followed by infusion for more than 24 hours.
maintenance infusion 0.2 to 1 mcg/kg/ Continuous respiratory monitoring.
hr titrated to effect.