Page 204 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 204
Cardiovascular Assessment and Monitoring 181
Capillary beds of
lungs where gas
exchange occurs
Pulmonary Pulmonary
arteries veins
Pulmonary circuit
Superior vena cava
Aorta and
Inferior vena cava Left branches
atrium
Right
atrium Left
ventricle Oxygenated blood from
Deoxygenated blood Right the lungs to the whole body
returned to the lungs ventricle
Systemic circuit
Capillary beds of all
body tissues where
gas exchange occurs
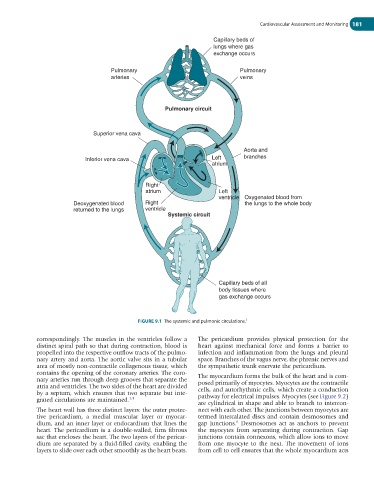
FIGURE 9.1 The systemic and pulmonic circulations. 3
correspondingly. The muscles in the ventricles follow a The pericardium provides physical protection for the
distinct spiral path so that during contraction, blood is heart against mechanical force and forms a barrier to
propelled into the respective outflow tracts of the pulmo- infection and inflammation from the lungs and pleural
nary artery and aorta. The aortic valve sits in a tubular space. Branches of the vagus nerve, the phrenic nerves and
area of mostly non-contractile collagenous tissue, which the sympathetic trunk enervate the pericardium.
contains the opening of the coronary arteries. The coro-
nary arteries run through deep grooves that separate the The myocardium forms the bulk of the heart and is com-
atria and ventricles. The two sides of the heart are divided posed primarily of myocytes. Myocytes are the con tractile
by a septum, which ensures that two separate but inte- cells, and autorhythmic cells, which create a conduction
grated circulations are maintained. 1,4 pathway for electrical impulses. Myocytes (see Figure 9.2)
are cylindrical in shape and able to branch to intercon-
The heart wall has three distinct layers: the outer protec- nect with each other. The junctions between myocytes are
tive pericardium, a medial muscular layer or myocar- termed intercalated discs and contain desmosomes and
6
dium, and an inner layer or endocardium that lines the gap junctions. Desmosomes act as anchors to prevent
heart. The pericardium is a double-walled, firm fibrous the myocytes from separating during contraction. Gap
sac that encloses the heart. The two layers of the pericar- junctions contain connexons, which allow ions to move
dium are separated by a fluid-filled cavity, enabling the from one myocyte to the next. The movement of ions
layers to slide over each other smoothly as the heart beats. from cell to cell ensures that the whole myocardium acts