Page 205 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 205
182 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
Red cell in
A band capillary
Capillary
I band endothelium
Invagination of Connective
sarcolemma by tissue
transverse tubule
Transverse tubule Intercalated
disk
Mitochondria
M line in Gap junction
H zone
Sarcolemma
Z line
Sarcomere Sarcoplasmic
reticulum
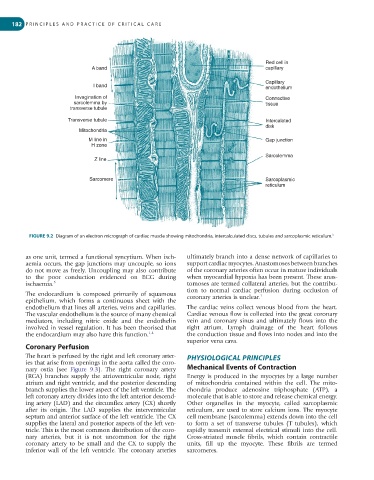
FIGURE 9.2 Diagram of an electron micrograph of cardiac muscle showing mitochondria, intercalculated discs, tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum. 5
as one unit, termed a functional syncytium. When isch- ultimately branch into a dense network of capillaries to
aemia occurs, the gap junctions may uncouple, so ions support cardiac myocytes. Anastomoses between branches
do not move as freely. Uncoupling may also contribute of the coronary arteries often occur in mature individuals
to the poor conduction evidenced on ECG during when myocardial hypoxia has been present. These anas-
ischaemia. 5 tomoses are termed collateral arteries, but the contribu-
tion to normal cardiac perfusion during occlusion of
The endocardium is composed primarily of squamous coronary arteries is unclear. 1
epithelium, which forms a continuous sheet with the
endothelium that lines all arteries, veins and capillaries. The cardiac veins collect venous blood from the heart.
The vascular endothelium is the source of many chemical Cardiac venous flow is collected into the great coronary
mediators, including nitric oxide and the endothelin vein and coronary sinus and ultimately flows into the
involved in vessel regulation. It has been theorised that right atrium. Lymph drainage of the heart follows
the endocardium may also have this function. 1,4 the conduction tissue and flows into nodes and into the
superior vena cava.
Coronary Perfusion
The heart is perfused by the right and left coronary arter- PHYSIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES
ies that arise from openings in the aorta called the coro-
nary ostia (see Figure 9.3). The right coronary artery Mechanical Events of Contraction
(RCA) branches supply the atrioventricular node, right Energy is produced in the myocytes by a large number
atrium and right ventricle, and the posterior descending of mitochondria contained within the cell. The mito-
branch supplies the lower aspect of the left ventricle. The chondria produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a
left coronary artery divides into the left anterior descend- molecule that is able to store and release chemical energy.
ing artery (LAD) and the circumflex artery (CX) shortly Other organelles in the myocyte, called sarcoplasmic
after its origin. The LAD supplies the interventricular reticulum, are used to store calcium ions. The myocyte
septum and anterior surface of the left ventricle. The CX cell membrane (sarcolemma) extends down into the cell
supplies the lateral and posterior aspects of the left ven- to form a set of transverse tubules (T tubules), which
tricle. This is the most common distribution of the coro- rapidly transmit external electrical stimuli into the cell.
nary arteries, but it is not uncommon for the right Cross-striated muscle fibrils, which contain contractile
coronary artery to be small and the CX to supply the units, fill up the myocyte. These fibrils are termed
inferior wall of the left ventricle. The coronary arteries sarcomeres.