Page 208 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 208
Cardiovascular Assessment and Monitoring 185
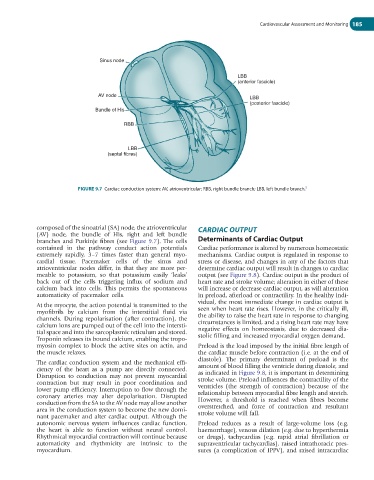
Sinus node
LBB
(anterior fascicle)
AV node LBB
(posterior fascicle)
Bundle of His
RBB
LBB
(septal fibres)
FIGURE 9.7 Cardiac conduction system: AV, atrioventricular; RBB, right bundle branch; LBB, left bundle branch. 5
composed of the sinoatrial (SA) node, the atrioventricular CARDIAC OUTPUT
(AV) node, the bundle of His, right and left bundle
branches and Purkinje fibres (see Figure 9.7). The cells Determinants of Cardiac Output
contained in the pathway conduct action potentials Cardiac performance is altered by numerous homeostatic
extremely rapidly, 3–7 times faster than general myo- mechanisms. Cardiac output is regulated in response to
cardial tissue. Pacemaker cells of the sinus and stress or disease, and changes in any of the factors that
atrioventricular nodes differ, in that they are more per- determine cardiac output will result in changes to cardiac
meable to potassium, so that potassium easily ‘leaks’ output (see Figure 9.8). Cardiac output is the product of
back out of the cells triggering influx of sodium and heart rate and stroke volume; alteration in either of these
calcium back into cells. This permits the spontaneous will increase or decrease cardiac output, as will alteration
automaticity of pacemaker cells. in preload, afterload or contractility. In the healthy indi-
vidual, the most immediate change in cardiac output is
At the myocyte, the action potential is transmitted to the
myofibrils by calcium from the interstitial fluid via seen when heart rate rises. However, in the critically ill,
channels. During repolarisation (after contraction), the the ability to raise the heart rate in response to changing
calcium ions are pumped out of the cell into the intersti- circumstances is limited, and a rising heart rate may have
tial space and into the sarcoplasmic reticulum and stored. negative effects on homeostasis, due to decreased dia-
Troponin releases its bound calcium, enabling the tropo- stolic filling and increased myocardial oxygen demand.
myosin complex to block the active sites on actin, and Preload is the load imposed by the initial fibre length of
the muscle relaxes. the cardiac muscle before contraction (i.e. at the end of
diastole). The primary determinant of preload is the
The cardiac conduction system and the mechanical effi- amount of blood filling the ventricle during diastole, and
ciency of the heart as a pump are directly connected. as indicated in Figure 9.8, it is important in determining
Disruption to conduction may not prevent myocardial stroke volume. Preload influences the contractility of the
contraction but may result in poor coordination and ventricles (the strength of contraction) because of the
lower pump efficiency. Interruption to flow through the relationship between myocardial fibre length and stretch.
coronary arteries may alter depolarisation. Disrupted However, a threshold is reached when fibres become
conduction from the SA to the AV node may allow another overstretched, and force of contraction and resultant
area in the conduction system to become the new domi- stroke volume will fall.
nant pacemaker and alter cardiac output. Although the
autonomic nervous system influences cardiac function, Preload reduces as a result of large-volume loss (e.g.
the heart is able to function without neural control. haemorrhage), venous dilation (e.g. due to hyperthermia
Rhythmical myocardial contraction will continue because or drugs), tachycardias (e.g. rapid atrial fibrillation or
automaticity and rhythmicity are intrinsic to the supraventricular tachycardias), raised intrathoracic pres-
myocardium. sures (a complication of IPPV), and raised intracardiac