Page 248 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 248
Cardiovascular Alterations and Management 225
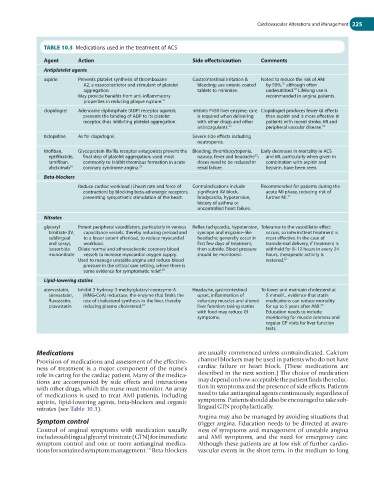
TABLE 10.3 Medications used in the treatment of ACS
Agent Action Side effects/caution Comments
Antiplatelet agents
aspirin Prevents platelet synthesis of thromboxane Gastrointestinal irritation & Noted to reduce the risk of AMI
A2, a vasoconstrictor and stimulant of platelet bleeding; use enteric-coated by 50%, although often
30
aggregation. tablets to minimise. underutilised. Lifelong use is
33
May provide benefits from anti-inflammatory recommended in angina patients.
properties in reducing plaque rupture. 31
clopidogrel Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) receptor agonist; Inhibits P450 liver enzyme; care Clopidogrel produces fewer GI effects
prevents the binding of ADP to its platelet is required when delivering than aspirin and is more effective in
receptor, thus inhibiting platelet aggregation. with other drugs and other patients with recent stroke, MI and
anticoagulants. 22 peripheral vascular disease. 34
ticlopidine As for clopidogrel. Severe side effects including
neutropenia.
tirofiban, Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor antagonists prevent the Bleeding, thrombocytopenia, Early decreases in mortality in ACS
eptifibatide, final step of platelet aggregation; used most nausea, fever and headache ; and MI, particularly when given in
22
lamifiban, commonly to inhibit thrombus formation in acute doses need to be reduced in combination with aspirin and
abciximab 36 coronary syndrome angina. 35 renal failure. heparin, have been seen.
Beta-blockers
Reduce cardiac workload (↓heart rate and force of Contraindications include Recommended for patients during the
contraction) by blocking beta-adrenergic receptors, significant AV block, acute MI phase, reducing risk of
preventing sympathetic stimulation of the heart. bradycardia, hypotension, further MI. 37
history of asthma or
uncontrolled heart failure.
Nitrates
glyceryl Potent peripheral vasodilators, particularly in venous Reflex tachycardia, hypotension, Tolerance to the vasodilator effect
trinitrate (IV, capacitance vessels, thereby reducing preload and syncope and migraine-like occurs, so intermittent treatment is
sublingual to a lesser extent afterload, to reduce myocardial headache; generally occur in most effective. In the case of
and spray), workload. first few days of treatment, transdermal delivery, if treatment is
isosorbide Dilate normal and atherosclerotic coronary blood then subside. Blood pressure withheld for 8–12 hours in every 24
mononitrate vessels to increase myocardial oxygen supply. should be monitored. hours, therapeutic activity is
Used to manage unstable angina and reduce blood restored. 22
pressure in the critical care setting, where there is
some evidence for symptomatic relief. 38
Lipid-lowering statins
atorvastatin, Inhibit 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme-A Headache, gastrointestinal To lower and maintain cholesterol at
simvastatin, (HMG-CoA) reductase, the enzyme that limits the upset, inflammation of 5 mmol/L, evidence that statin
fluvastatin, rate of cholesterol synthesis in the liver, thereby voluntary muscles and altered medications can reduce mortality
39
pravastatin reducing plasma cholesterol. 22 liver function; taking statins for up to 5 years after AMI.
with food may reduce GI Education needs to include
symptoms. monitoring for muscle soreness and
regular GP visits for liver function
tests.
Medications are usually commenced unless contraindicated. Calcium
Provision of medications and assessment of the effective- channel blockers may be used in patients who do not have
ness of treatment is a major component of the nurse’s cardiac failure or heart block. (These medications are
role in caring for the cardiac patient. Many of the medica- described in the next section.) The choice of medication
tions are accompanied by side effects and interactions may depend on how acceptable the patient finds the reduc-
with other drugs, which the nurse must monitor. An array tion in symptoms and the presence of side effects. Patients
of medications is used to treat AMI patients, including need to take antianginal agents continuously, regardless of
aspirin, lipid-lowering agents, beta-blockers and organic symptoms. Patients should also be encouraged to take sub-
nitrates (see Table 10.3). lingual GTN prophylactically.
Angina may also be managed by avoiding situations that
Symptom control trigger angina. Education needs to be directed at aware-
Control of anginal symptoms with medication usually ness of symptoms and management of unstable angina
includes sublingual glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) for immediate and AMI symptoms, and the need for emergency care.
symptom control and one or more antianginal medica- Although these patients are at low risk of further cardio-
18
tions for sustained symptom management. Beta-blockers vascular events in the short term, in the medium to long