Page 252 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 252
Cardiovascular Alterations and Management 229
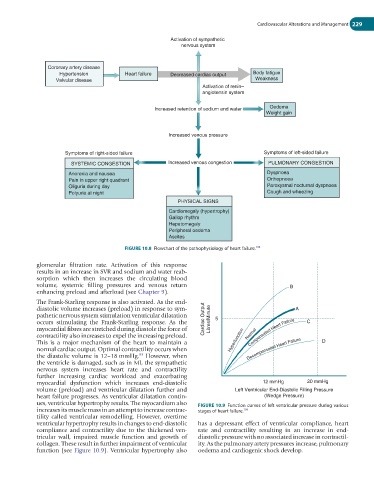
Activation of sympathetic
nervous system
Coronary artery disease
Hypertension Heart failure Decreased cardiac output Body fatigue
Valvular disease Weakness
Activation of renin–
angiotensin system
Increased retention of sodium and water Oedema
Weight gain
Increased venous pressure
Symptoms of right-sided failure Symptoms of left-sided failure
SYSTEMIC CONGESTION Increased venous congestion PULMONARY CONGESTION
Anorexia and nausea Dyspnoea
Pain in upper right quadrant Orthopnoea
Oliguria during day Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea
Polyuria at night Cough and wheezing
PHYSICAL SIGNS
Cardiomegaly (hypertrophy)
Gallop rhythm
Hepatomegaly
Peripheral oedema
Ascites
104
FIGURE 10.8 Flowchart of the pathophysiology of heart failure.
glomerular filtration rate. Activation of this response
results in an increase in SVR and sodium and water reab-
sorption which then increases the circulating blood
volume, systemic filling pressures and venous return B
enhancing preload and afterload (see Chapter 9).
The Frank-Starling response is also activated. As the end-
diastolic volume increases (preload) in response to sym- A
pathetic nervous system stimulation ventricular dilatation
Compensated Heart Failure
occurs stimulating the Frank-Starling response. As the Cardiac Output Litres/Minute 5 C
myocardial fibres are stretched during diastole the force of
contractility also increases to expel the increasing preload. Normal
This is a major mechanism of the heart to maintain a Hyperfunction D
normal cardiac output. Optimal contractility occurs when Decompensated Heart Failure
63
the diastolic volume is 12–18 mmHg. However, when
the ventricle is damaged, such as in MI, the sympathetic
nervous system increases heart rate and contractility
further increasing cardiac workload and exacerbating
myocardial dysfunction which increases end-diastolic 12 mmHg 20 mmHg
volume (preload) and ventricular dilatation further and Left Ventricular End-Diastolic Filling Pressure
heart failure progresses. As ventricular dilatation contin- (Wedge Pressure)
ues, ventricular hypertrophy results. The myocardium also FIGURE 10.9 Function curves of left ventricular pressure during various
increases its muscle mass in an attempt to increase contrac- stages of heart failure.
109
tility called ventricular remodelling. However, overtime
ventricular hypertrophy results in changes to end-diastolic has a depressant effect of ventricular compliance, heart
compliance and contractility due to the thickened ven- rate and contractility resulting in an increase in end-
tricular wall, impaired muscle function and growth of diastolic pressure with no associated increase in contractil-
collagen. These result in further impairment of ventricular ity. As the pulmonary artery pressures increase, pulmonary
function (see Figure 10.9). Ventricular hypertrophy also oedema and cardiogenic shock develop.