Page 243 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 243
220 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
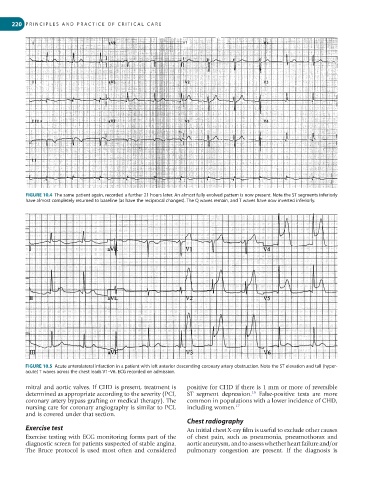
FIGURE 10.4 The same patient again, recorded a further 21 hours later. An almost fully evolved pattern is now present. Note the ST segments inferiorly
have almost completely returned to baseline (as have the reciprocal changes). The Q waves remain, and T waves have now inverted inferiorly.
FIGURE 10.5 Acute anterolateral infarction in a patient with left anterior descending coronary artery obstruction. Note the ST elevation and tall (hyper-
acute) T waves across the chest leads V1–V6. ECG recorded on admission.
mitral and aortic valves. If CHD is present, treatment is positive for CHD if there is 1 mm or more of reversible
16
determined as appropriate according to the severity (PCI, ST segment depression. False-positive tests are more
coronary artery bypass grafting or medical therapy). The common in populations with a lower incidence of CHD,
nursing care for coronary angiography is similar to PCI, including women. 17
and is covered under that section.
Chest radiography
Exercise test An initial chest X-ray film is useful to exclude other causes
Exercise testing with ECG monitoring forms part of the of chest pain, such as pneumonia, pneumothorax and
diagnostic screen for patients suspected of stable angina. aortic aneurysm, and to assess whether heart failure and/or
The Bruce protocol is used most often and considered pulmonary congestion are present. If the diagnosis is