Page 256 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 256
Cardiovascular Alterations and Management 233
● urinalysis for specific gravity and proteinuria.
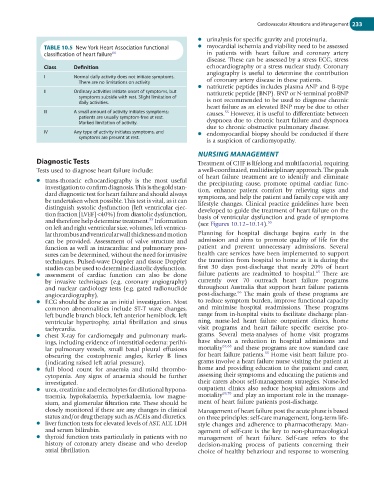
TABLE 10.5 New York Heart Association functional ● myocardial ischemia and viability need to be assessed
classification of heart failure 64 in patients with heart failure and coronary artery
disease. These can be assessed by a stress ECG, stress
Class Definition echocardiography or a stress nuclear study. Coronary
angiography is useful to determine the contribution
I Normal daily activity does not initiate symptoms.
There are no limitations on activity of coronary artery disease in these patients.
● natriuretic peptides includes plasma ANP and B-type
II Ordinary activities initiate onset of symptoms, but natriuretic peptide (BNP). BNP or N-terminal proBNP
symptoms subside with rest. Slight limitation of
daily activities. is not recommended to be used to diagnose chronic
heart failure as an elevated BNP may be due to other
III A small amount of activity initiates symptoms; causes. However, it is useful to differentiate between
55
patients are usually symptom-free at rest.
Marked limitation of activity. dyspnoea due to chronic heart failure and dyspnoea
due to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
IV Any type of activity initiates symptoms, and ● endomyocardial biopsy should be conducted if there
symptoms are present at rest.
is a suspicion of cardiomyopathy.
NURSING MANAGEMENT
Diagnostic Tests Treatment of CHF is lifelong and multifactorial, requiring
Tests used to diagnose heart failure include: a well-coordinated, multidisciplinary approach. The goals
of heart failure treatment are to identify and eliminate
● trans-thoracic echocardiography is the most useful the precipitating cause, promote optimal cardiac func-
investigation to confirm diagnosis. This is the gold stan- tion, enhance patient comfort by relieving signs and
dard diagnostic test for heart failure and should always symptoms, and help the patient and family cope with any
be undertaken when possible. This test is vital, as it can lifestyle changes. Clinical practice guidelines have been
distinguish systolic dysfunction (left ventricular ejec- developed to guide the treatment of heart failure on the
tion fraction [LVEF] <40%) from diastolic dysfunction, basis of ventricular dysfunction and grade of symptoms
55
and therefore help determine treatment. Information (see Figures 10.12–10.14). 55
on left and right ventricular size, volumes, left ventricu-
lar thrombus and ventricular wall thickness and motion Planning for hospital discharge begins early in the
can be provided. Assessment of valve structure and admission and aims to promote quality of life for the
function as well as intracardiac and pulmonary pres- patient and prevent unnecessary admissions. Several
sures can be determined, without the need for invasive health care services have been implemented to support
techniques. Pulsed-wave Doppler and tissue Doppler the transition from hospital to home as it is during the
studies can be used to determine diastolic dysfunction. first 30 days post-discharge that nearly 20% of heart
65
● assessment of cardiac function can also be done failure patients are readmitted to hospital. There are
by invasive techniques (e.g. coronary angiography) currently over 70 outreach heart failure programs
and nuclear cardiology tests (e.g. gated radionuclide throughout Australia that support heart failure patients
66
angiocardiography). post-discharge. The main goals of these programs are
● ECG should be done as an initial investigation. Most to reduce symptom burden, improve functional capacity
common abnormalities include ST-T wave changes, and minimise hospital readmissions. These programs
left bundle branch block, left anterior hemiblock, left range from in-hospital visits to facilitate discharge plan-
ventricular hypertrophy, atrial fibrillation and sinus ning, nurse-led heart failure outpatient clinics, home
tachycardia. visit programs and heart failure specific exercise pro-
● chest X-ray for cardiomegaly and pulmonary mark- grams. Several meta-analyses of home visit programs
ings, including evidence of interstitial oedema: perihi- have shown a reduction in hospital admissions and
lar pulmonary vessels, small basal pleural effusions mortality 67,68 and these programs are now standard care
55
obscuring the costophrenic angles, Kerley B lines for heart failure patients. Home visit heart failure pro-
(indicating raised left atrial pressure). grams involve a heart failure nurse visiting the patient at
● full blood count for anaemia and mild thrombo- home and providing education to the patient and carer,
cytopenia. Any signs of anaemia should be further assessing their symptoms and educating the patients and
investigated. their carers about self-management strategies. Nurse-led
● urea, creatinine and electrolytes for dilutional hypona- outpatient clinics also reduce hospital admissions and
traemia, hypokalaemia, hyperkalaemia, low magne- mortality 69,70 and play an important role in the manage-
sium, and glomerular filtration rate. These should be ment of heart failure patients post-discharge.
closely monitored if there are any changes in clinical Management of heart failure post the acute phase is based
status and/or drug therapy such as ACEIs and diuretics. on three principles: self-care management, long-term life-
● liver function tests for elevated levels of AST, ALT, LDH style changes and adherence to pharmacotherapy. Man-
and serum bilirubin. agement of self-care is the key to non-pharmacological
● thyroid function tests particularly in patients with no management of heart failure. Self-care refers to the
history of coronary artery disease and who develop decision-making process of patients concerning their
atrial fibrillation. choice of healthy behaviour and response to worsening