Page 259 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 259
236 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
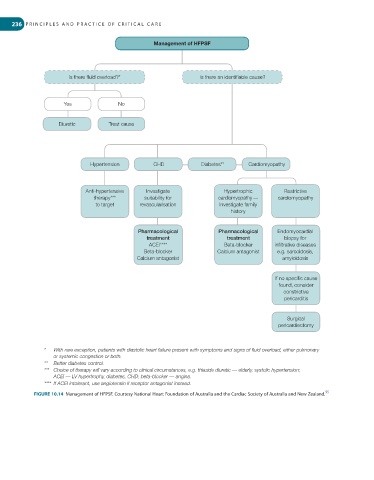
Management of HFPSF
Is there fl uid overload?* Is there an identifi able cause?
Yes No
Diuretic Treat cause
Hypertension CHD Diabetes** Cardiomyopathy
Anti-hypertensive Investigate Hypertrophic Restrictive
therapy*** suitability for cardiomyopathy — cardiomyopathy
to target revascularisation Investigate family
history
Pharmacological Pharmacological Endomyocardial
treatment treatment biopsy for
ACEI**** Beta-blocker infi ltrative diseases
Beta-blocker Calcium antagonist e.g. sarcoidosis,
Calcium antagonist amyloidosis
If no specifi c cause
found, consider
constrictive
pericarditis
Surgical
pericardiectomy
* With rare exception, patients with diastolic heart failure present with symptoms and signs of fl uid overload, either pulmonary
or systemic congestion or both.
** Better diabetes control.
*** Choice of therapy will vary according to clinical circumstances, e.g. thiazide diuretic — elderly, systolic hypertension;
ACEI — LV hypertrophy, diabetes, CHD; beta-blocker — angina.
**** If ACEI intolerant, use angiotensin II receptor antagonist instead.
55
FIGURE 10.14 Management of HFPSF. Courtesy National Heart Foundation of Australia and the Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand.