Page 276 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 276
Cardiac Rhythm Assessment and Management 253
FIGURE 11.1 Sinus rhythm, rate 78/min. All P waves are followed by QRS complexes of normal duration after a P-R interval of around 0.16 sec.
FIGURE 11.2 Sinus tachycardia. The rhythm is slightly irregular and varies between 105/min and 115/min.
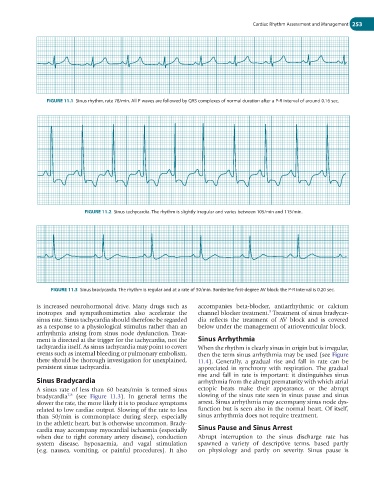
FIGURE 11.3 Sinus bradycardia. The rhythm is regular and at a rate of 50/min. Borderline first-degree AV block: the P-R interval is 0.20 sec.
is increased neurohormonal drive. Many drugs such as accompanies beta-blocker, antiarrhythmic or calcium
9
inotropes and sympathomimetics also accelerate the channel blocker treatment. Treatment of sinus bradycar-
sinus rate. Sinus tachycardia should therefore be regarded dia reflects the treatment of AV block and is covered
as a response to a physiological stimulus rather than an below under the management of atrioventricular block.
arrhythmia arising from sinus node dysfunction. Treat-
ment is directed at the trigger for the tachycardia, not the Sinus Arrhythmia
tachycardia itself. As sinus tachycardia may point to covert When the rhythm is clearly sinus in origin but is irregular,
events such as internal bleeding or pulmonary embolism, then the term sinus arrhythmia may be used (see Figure
there should be thorough investigation for unexplained, 11.4). Generally, a gradual rise and fall in rate can be
persistent sinus tachycardia. appreciated in synchrony with respiration. The gradual
rise and fall in rate is important: it distinguishes sinus
Sinus Bradycardia arrhythmia from the abrupt prematurity with which atrial
A sinus rate of less than 60 beats/min is termed sinus ectopic beats make their appearance, or the abrupt
7,8
bradycardia (see Figure 11.3). In general terms the slowing of the sinus rate seen in sinus pause and sinus
slower the rate, the more likely it is to produce symptoms arrest. Sinus arrhythmia may accompany sinus node dys-
related to low cardiac output. Slowing of the rate to less function but is seen also in the normal heart. Of itself,
than 50/min is commonplace during sleep, especially sinus arrhythmia does not require treatment.
in the athletic heart, but is otherwise uncommon. Brady-
cardia may accompany myocardial ischaemia (especially Sinus Pause and Sinus Arrest
when due to right coronary artery disease), conduction Abrupt interruption to the sinus discharge rate has
system disease, hypoxaemia, and vagal stimulation spawned a variety of descriptive terms, based partly
(e.g. nausea, vomiting, or painful procedures). It also on physiology and partly on severity. Sinus pause is