Page 279 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 279
256 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
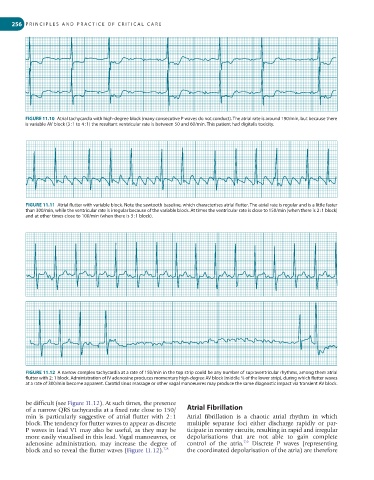
FIGURE 11.10 Atrial tachycardia with high-degree block (many consecutive P waves do not conduct). The atrial rate is around 190/min, but because there
is variable AV block (3 : 1 to 4 : 1) the resultant ventricular rate is between 50 and 60/min. This patient had digitalis toxicity.
FIGURE 11.11 Atrial flutter with variable block. Note the sawtooth baseline, which characterises atrial flutter. The atrial rate is regular and is a little faster
than 300/min, while the ventricular rate is irregular because of the variable block. At times the ventricular rate is close to 150/min (when there is 2 : 1 block)
and at other times close to 100/min (when there is 3 : 1 block).
FIGURE 11.12 A narrow complex tachycardia at a rate of 150/min in the top strip could be any number of supraventricular rhythms, among them atrial
flutter with 2 : 1 block. Administration of IV adenosine produces momentary high-degree AV block (middle ⅔ of the lower strip), during which flutter waves
at a rate of 300/min become apparent. Carotid sinus massage or other vagal manoeuvres may produce the same diagnostic impact via transient AV block.
be difficult (see Figure 11.12). At such times, the presence
of a narrow QRS tachycardia at a fixed rate close to 150/ Atrial Fibrillation
min is particularly suggestive of atrial flutter with 2 : 1 Atrial fibrillation is a chaotic atrial rhythm in which
block. The tendency for flutter waves to appear as discrete multiple separate foci either discharge rapidly or par-
P waves in lead V1 may also be useful, as they may be ticipate in reentry circuits, resulting in rapid and irregular
more easily visualised in this lead. Vagal manoeuvres, or depolarisations that are not able to gain complete
7,9
adenosine administration, may increase the degree of control of the atria. Discrete P waves (representing
block and so reveal the flutter waves (Figure 11.12). 7,8 the coordinated depolarisation of the atria) are therefore