Page 278 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 278
Cardiac Rhythm Assessment and Management 255
FIGURE 11.7 Sinus rhythm with frequent atrial ectopics. The notched P waves at a rate of 75–80/min are the Ps of the dominant sinus rhythm, while the
more rapidly firing P waves with peaked configurations are the atrial ectopic beats. Note that the ectopic P waves have some variability in their shapes
and firing rate. They should therefore be described as multifocal atrial ectopics.
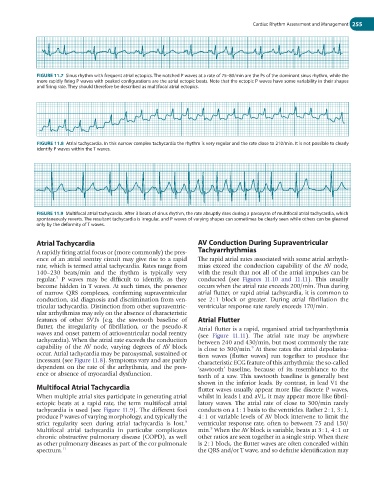
FIGURE 11.8 Atrial tachycardia. In this narrow complex tachycardia the rhythm is very regular and the rate close to 210/min. It is not possible to clearly
identify P waves within the T waves.
FIGURE 11.9 Multifocal atrial tachycardia. After 3 beats of sinus rhythm, the rate abruptly rises during a paroxysm of multifocal atrial tachycardia, which
spontaneously reverts. The resultant tachycardia is irregular, and P waves of varying shapes can sometimes be clearly seen while others can be gleaned
only by the deformity of T waves.
Atrial Tachycardia AV Conduction During Supraventricular
A rapidly firing atrial focus or (more commonly) the pres- Tachyarrhythmias
ence of an atrial reentry circuit may give rise to a rapid The rapid atrial rates associated with some atrial arrhyth-
rate, which is termed atrial tachycardia. Rates range from mias exceed the conduction capability of the AV node,
140–230 beats/min and the rhythm is typically very with the result that not all of the atrial impulses can be
5
regular. P waves may be difficult to identify, as they conducted (see Figures 11.10 and 11.11). This usually
become hidden in T waves. At such times, the presence occurs when the atrial rate exceeds 200/min. Thus during
of narrow QRS complexes, confirming supraventricular atrial flutter, or rapid atrial tachycardia, it is common to
conduction, aid diagnosis and discrimination from ven- see 2 : 1 block or greater. During atrial fibrillation the
tricular tachycardia. Distinction from other supraventric- ventricular response rate rarely exceeds 170/min.
ular arrhythmias may rely on the absence of characteristic
features of other SVTs (e.g. the sawtooth baseline of Atrial Flutter
flutter, the irregularity of fibrillation, or the pseudo-R Atrial flutter is a rapid, organised atrial tachyarrhythmia
waves and onset pattern of atrioventricular nodal reentry (see Figure 11.11). The atrial rate may be anywhere
tachycardia). When the atrial rate exceeds the conduction between 240 and 430/min, but most commonly the rate
capability of the AV node, varying degrees of AV block is close to 300/min. At these rates the atrial depolarisa-
9
occur. Atrial tachycardia may be paroxysmal, sustained or tion waves (flutter waves) run together to produce the
incessant (see Figure 11.8). Symptoms vary and are partly characteristic ECG feature of this arrhythmia: the so-called
dependent on the rate of the arrhythmia, and the pres- ‘sawtooth’ baseline, because of its resemblance to the
ence or absence of myocardial dysfunction. teeth of a saw. This sawtooth baseline is generally best
shown in the inferior leads. By contrast, in lead V1 the
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia flutter waves usually appear more like discrete P waves,
When multiple atrial sites participate in generating atrial whilst in leads I and aVL, it may appear more like fibril-
ectopic beats at a rapid rate, the term multifocal atrial latory waves. The atrial rate of close to 300/min rarely
tachycardia is used (see Figure 11.9). The different foci conducts on a 1 : 1 basis to the ventricles. Rather 2 : 1, 3 : 1,
produce P waves of varying morphology, and typically the 4 : 1 or variable levels of AV block intervene to limit the
9
strict regularity seen during atrial tachycardia is lost. ventricular response rate, often to between 75 and 150/
9
Multifocal atrial tachycardia in particular complicates min. When the AV block is variable, beats at 3 : 1, 4 : 1 or
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), as well other ratios are seen together in a single strip. When there
as other pulmonary diseases as part of the cor pulmonale is 2 : 1 block, the flutter waves are often concealed within
spectrum. 11 the QRS and/or T wave, and so definite identification may