Page 458 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 458
Neurological Assessment and Monitoring 435
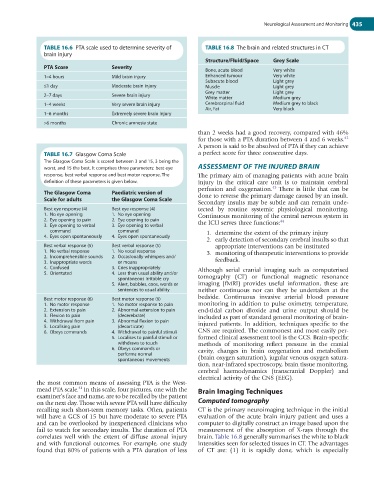
TABLE 16.6 PTA scale used to determine severity of TABLE 16.8 The brain and related structures in CT
brain injury
Structure/Fluid/Space Grey Scale
PTA Score Severity Bone, acute blood Very white
1–4 hours Mild brain injury Enhanced tumour Very white
Subacute blood Light grey
≤1 day Moderate brain injury Muscle Light grey
Grey matter Light grey
2–7 days Severe brain injury White matter Medium grey
1–4 weeks Very severe brain injury Cerebrospinal fluid Medium grey to black
Air, Fat Very black
1–6 months Extremely severe brain injury
>6 months Chronic amnesia state
than 2 weeks had a good recovery, compared with 46%
42
for those with a PTA duration between 4 and 6 weeks.
A person is said to be absolved of PTA if they can achieve
TABLE 16.7 Glasgow Coma Scale a perfect score for three consecutive days.
The Glasgow Coma Scale is scored between 3 and 15, 3 being the
worst, and 15 the best. It comprises three parameters: best eye ASSESSMENT OF THE INJURED BRAIN
response, best verbal response and best motor response. The The primary aim of managing patients with acute brain
definition of these parameters is given below. injury in the critical care unit is to maintain cerebral
43
perfusion and oxygenation. There is little that can be
The Glasgow Coma Paediatric version of
Scale for adults the Glasgow Coma Scale done to reverse the primary damage caused by an insult.
Secondary insults may be subtle and can remain unde-
Best eye response (4) Best eye response (4) tected by routine systemic physiological monitoring.
1. No eye opening 1. No eye opening Continuous monitoring of the central nervous system in
2. Eye opening to pain 2. Eye opening to pain 44
3. Eye opening to verbal 3. Eye opening to verbal the ICU serves three functions:
command command 1. determine the extent of the primary injury
4. Eyes open spontaneously 4. Eyes open spontaneously
2. early detection of secondary cerebral insults so that
Best verbal response (5) Best verbal response (5) appropriate interventions can be instituted
1. No verbal response 1. No vocal response 3. monitoring of therapeutic interventions to provide
2. Incomprehensible sounds 2. Occasionally whimpers and/
3. Inappropriate words or moans feedback.
4. Confused 3. Cries inappropriately Although serial cranial imaging such as computerised
5. Orientated 4. Less than usual ability and/or
spontaneous irritable cry tomography (CT) or functional magnetic resonance
5. Alert, babbles, coos, words or imaging (fMRI) provides useful information, these are
sentences to usual ability neither continuous nor can they be undertaken at the
Best motor response (6) Best motor response (6) bedside. Continuous invasive arterial blood pressure
1. No motor response 1. No motor response to pain monitoring in addition to pulse oximetry, temperature,
2. Extension to pain 2. Abnormal extension to pain end-tidal carbon dioxide and urine output should be
3. Flexion to pain (decerebrate) included as part of standard general monitoring of brain-
4. Withdrawal from pain 3. Abnormal flexion to pain
5. Localising pain (decorticate) injured patients. In addition, techniques specific to the
6. Obeys commands 4. Withdrawal to painful stimuli CNS are required. The commonest and most easily per-
5. Localises to painful stimuli or formed clinical assessment tool is the GCS. Brain-specific
withdraws to touch methods of monitoring reflect pressure in the cranial
6. Obeys commands or cavity, changes in brain oxygenation and metabolism
performs normal
spontaneous movements (brain oxygen saturation), jugular venous oxygen satura-
tion, near-infrared spectroscopy, brain tissue monitoring,
cerebral haemodynamics (transcranial Doppler) and
electrical activity of the CNS (EEG).
the most common means of assessing PTA is the West-
41
mead PTA scale. In this scale, four pictures, one with the Brain Imaging Techniques
examiner’s face and name, are to be recalled by the patient
on the next day. Those with severe PTA will have difficulty Computed tomography
recalling such short-term memory tasks. Often, patients CT is the primary neuroimaging technique in the initial
will have a GCS of 15 but have moderate to severe PTA evaluation of the acute brain injury patient and uses a
and can be overlooked by inexperienced clinicians who computer to digitally construct an image based upon the
fail to watch for secondary insults. The duration of PTA measurement of the absorption of X-rays through the
correlates well with the extent of diffuse axonal injury brain. Table 16.8 generally summarises the white to black
and with functional outcomes. For example, one study intensities seen for selected tissues in CT. The advantages
found that 80% of patients with a PTA duration of less of CT are: (1) it is rapidly done, which is especially