Page 453 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 453
430 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
C-2
C-2
C-3
C-3 C-4
C-4 C-5
T-2 C-6
C-5 T-3 T-2
T-4 T-6 T-3
T-5 T-7
T-6 T-8 C-7
T-7 T-9
T-1
T-8 T-10
T-9 T-11 C-8
C-6 T-10 T-12 T-1
T-11
T-12 C-6
C-7 L-1 L-1
L-1 S-3 L-1
S-3 S-3
L-2 L-2
S-4
C-8 L-2 L-2
L-3 L-3
S-2 S-2
L-5 L-5 L-4
L-4 L-4
L-5
S-1 S-1
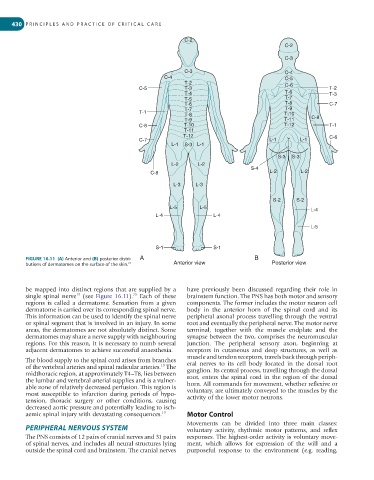
FIGURE 16.11 (A) Anterior and (B) posterior distri- A B
25
butions of dermatomes on the surface of the skin. Anterior view Posterior view
be mapped into distinct regions that are supplied by a have previously been discussed regarding their role in
25
19
single spinal nerve (see Figure 16.11). Each of these brainstem function. The PNS has both motor and sensory
regions is called a dermatome. Sensation from a given components. The former includes the motor neuron cell
dermatome is carried over its corresponding spinal nerve. body in the anterior horn of the spinal cord and its
This information can be used to identify the spinal nerve peripheral axonal process travelling through the ventral
or spinal segment that is involved in an injury. In some root and eventually the peripheral nerve. The motor nerve
areas, the dermatomes are not absolutely distinct. Some terminal, together with the muscle endplate and the
dermatomes may share a nerve supply with neighbouring synapse between the two, comprises the neuromuscular
regions. For this reason, it is necessary to numb several junction. The peripheral sensory axon, beginning at
adjacent dermatomes to achieve successful anaesthesia. receptors in cutaneous and deep structures, as well as
muscle and tendon receptors, travels back through periph-
The blood supply to the spinal cord arises from branches eral nerves to its cell body located in the dorsal root
19
of the vertebral arteries and spinal radicular arteries. The ganglion. Its central process, travelling through the dorsal
midthoracic region, at approximately T4–T8, lies between root, enters the spinal cord in the region of the dorsal
the lumbar and vertebral arterial supplies and is a vulner- horn. All commands for movement, whether reflexive or
able zone of relatively decreased perfusion. This region is voluntary, are ultimately conveyed to the muscles by the
most susceptible to infarction during periods of hypo- activity of the lower motor neurons.
tension, thoracic surgery or other conditions, causing
decreased aortic pressure and potentially leading to isch-
aemic spinal injury with devastating consequences. 19 Motor Control
Movements can be divided into three main classes:
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM voluntary activity, rhythmic motor patterns, and reflex
The PNS consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs responses. The highest-order activity is voluntary move-
of spinal nerves, and includes all neural structures lying ment, which allows for expression of the will and a
outside the spinal cord and brainstem. The cranial nerves purposeful response to the environment (e.g. reading,