Page 455 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 455
432 P R I N C I P L E S A N D P R A C T I C E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
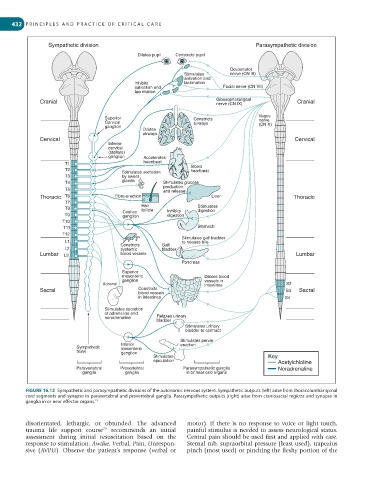
Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division
Dilates pupil Constricts pupil
Oculomotor
Stimulates nerve (CN III)
salivation and
Inhibits lacrimation
salivation and Facial nerve (CN VII)
lacrimation
Cranial Glossopharangeal Cranial
nerve (CN IX)
Superior Constricts Vagus
nerve
Cervical airways (CN X)
ganglion
Dilates
airways
Cervical Cervical
Inferior
cervical
(stellate)
ganglion Accelerates
T1 heartbeat Slows
T2 Stimulates secretion heartbeat
T3 by sweat
T4 glands Stimulates glucose
production
T5 and release
Thoracic T6 Fibre-erection Liver Thoracic
T7
T8 Hair Inhibits Stimulates
follicle
digestion
T9 Coeliac digestion
ganglion
T10
T11 Stomach
T12
Stimulates gall bladder
L1 to release bile
Constricts Gall
L2 systemic bladder
Lumbar L3 blood vessels Lumbar
Pancreas
Superior
mesenteric Dilates blood
ganglion vessels in
Adrenal intestines S2
Sacral Constricts S3 Sacral
blood vessels
in intestines S4
Stimulates secretion
of adrenaline and
noradrenaline Relaxes urinary
bladder
Stimulates urinary
bladder to contract
Stimulates penile
Inferior erection
Sympathetic mesenteric
trunk ganglion
Stimulates Key
ejaculation Acetylchloline
Paravertebral Provertebral Parasympathetic ganglia Noradrenaline
ganglia ganglia in or near end organs
FIGURE 16.12 Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic outputs (left) arise from thoracolumbar spinal
cord segments and synapse in paravertebral and prevertebral ganglia. Parasympathetic outputs (right) arise from craniosacral regions and synapse in
15
ganglia in or near effector organs.
disorientated, lethargic, or obtunded. The advanced motor). If there is no response to voice or light touch,
26
trauma life support course recommends an initial painful stimulus is needed to assess neurological status.
assessment during initial resuscitation based on the Central pain should be used first and applied with care.
response to stimulation: Awake, Verbal, Pain, Unrespon- Sternal rub, supraorbital pressure (least used), trapezius
sive (AVPU). Observe the patient’s response (verbal or pinch (most used) or pinching the fleshy portion of the