Page 54 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 54
Resourcing Critical Care 31
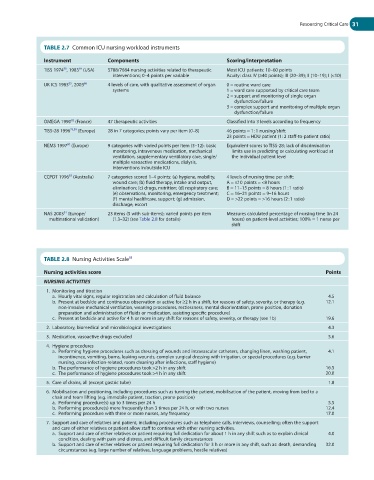
TABLE 2.7 Common ICU nursing workload instruments
Instrument Components Scoring/interpretation
84
TISS 1974 , 1983 (USA) 5788/7684 nursing activities related to therapeutic Most ICU patients: 10–60 points
88
interventions; 0–4 points per variable Acuity: class IV (≥40 points); III (20–39); II (10–19); I (<10)
UK ICS 1983 , 2003 86 4 levels of care, with qualitative assessment of organ 0 = routine ward care
85
systems 1 = ward care supported by critical care team
2 = support and monitoring of single organ
dysfunction/failure
3 = complex support and monitoring of multiple organ
dysfunction/failure
OMEGA 1990 (France) 47 therapeutic activities Classified into 3 levels according to frequency
82
TISS-28 1996 79,89 (Europe) 28 in 7 categories; points vary per item (0–8) 46 points = 1 : 1 nursing/shift
23 points = HDU patient (1 : 2 staff-to-patient ratio)
80
NEMS 1997 (Europe) 9 categories with varied points per item (3–12): basic Equivalent scores to TISS-28; lack of discrimination
monitoring, intravenous medication, mechanical limits use in predicting or calculating workload at
ventilation, supplementary ventilatory care, single/ the individual patient level
multiple vasoactive medications, dialysis,
interventions in/outside ICU
CCPDT 1996 (Australia) 7 categories scored 1–4 points: (a) hygiene, mobility, 4 levels of nursing time per shift:
83
wound care; (b) fluid therapy, intake and output, A = ≤10 points = <8 hours
elimination; (c) drugs, nutrition; (d) respiratory care; B = 11–15 points = 8 hours (1 : 1 ratio)
(e) observations, monitoring, emergency treatment; C = 16–21 points = 9–16 hours
(f) mental healthcare, support; (g) admission, D = >22 points = >16 hours (2 : 1 ratio)
discharge, escort
NAS 2003 (Europe/ 23 items (5 with sub-items); varied points per item Measures calculated percentage of nursing time (in 24
81
multinational validation) (1.3–32) (see Table 2.8 for details) hours) on patient-level activities; 100% = 1 nurse per
shift
81
TABLE 2.8 Nursing Activities Scale
Nursing activities score Points
NURSING ACTIVITIES
1. Monitoring and titration
a. Hourly vital signs, regular registration and calculation of fluid balance 4.5
b. Present at bedside and continuous observation or active for ≥2 h in a shift, for reasons of safety, severity, or therapy (e.g. 12.1
non-invasive mechanical ventilation, weaning procedures, restlessness, mental disorientation, prone position, donation
preparation and administration of fluids or medication, assisting specific procedure)
c. Present at bedside and active for 4 h or more in any shift for reasons of safety, severity, or therapy (see 1b) 19.6
2. Laboratory, biomedical and microbiological investigations 4.3
3. Medication, vasoactive drugs excluded 5.6
4. Hygiene procedures
a. Performing hygiene procedures such as dressing of wounds and intravascular catheters, changing linen, washing patient, 4.1
incontinence, vomiting, burns, leaking wounds, complex surgical dressing with irrigation, or special procedures (e.g. barrier
nursing, cross-infection-related, room cleaning after infections, staff hygiene)
b. The performance of hygiene procedures took >2 h in any shift 16.5
c. The performance of hygiene procedures took >4 h in any shift 20.0
5. Care of drains, all (except gastric tube) 1.8
6. Mobilisation and positioning, including procedures such as turning the patient, mobilisation of the patient, moving from bed to a
chair and team lifting (e.g. immobile patient, traction, prone position)
a. Performing procedure(s) up to 3 times per 24 h 5.5
b. Performing procedure(s) more frequently than 3 times per 24 h, or with two nurses 12.4
c. Performing procedure with three or more nurses, any frequency 17.0
7. Support and care of relatives and patient, including procedures such as telephone calls, interviews, counselling; often the support
and care of either relatives or patient allow staff to continue with other nursing activities.
a. Support and care of either relatives or patient requiring full dedication for about 1 h in any shift such as to explain clinical 4.0
condition, dealing with pain and distress, and difficult family circumstances
b. Support and care of either relatives or patient requiring full dedication for 3 h or more in any shift, such as: death, demanding 32.0
circumstances (e.g. large number of relatives, language problems, hostile relatives)