Page 55 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 55
32 S C O P E O F C R I T I C A L C A R E
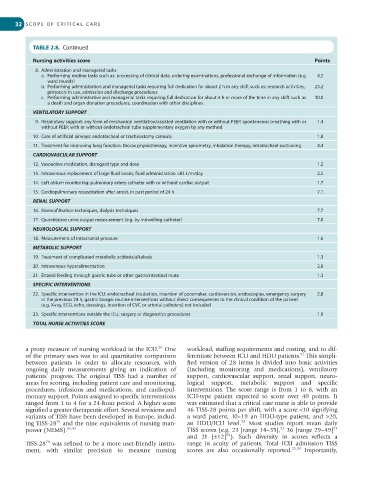
TABLE 2.8, Continued
Nursing activities score Points
8. Administration and managerial tasks
a. Performing routine tasks such as: processing of clinical data, ordering examinations, professional exchange of information (e.g. 4.2
ward rounds)
b. Performing administration and managerial tasks requiring full dedication for about 2 h in any shift such as: research activities, 23.2
protocols in use, admission and discharge procedures
c. Performing administrative and managerial tasks requiring full dedication for about 4 h or more of the time in any shift such as 30.0
a death and organ donation procedures, coordination with other disciplines
VENTILATORY SUPPORT
9. Respiratory support: any form of mechanical ventilation/assisted ventilation with or without PEEP, spontaneous breathing with or 1.4
without PEEP, with or without endotracheal tube supplementary oxygen by any method
10. Care of artificial airways: endotracheal or tracheostomy cannula 1.8
11. Treatment for improving lung function: thorax physiotherapy, incentive spirometry, inhalation therapy, intratracheal suctioning 4.4
CARDIOVASCULAR SUPPORT
12. Vasoactive medication, disregard type and dose 1.2
13. Intravenous replacement of large fluid losses, fluid administration >83 L/m/day 2.5
14. Left atrium monitoring: pulmonary artery catheter with or without cardiac output 1.7
15. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation after arrest, in past period of 24 h 7.1
RENAL SUPPORT
16. Haemofiltration techniques, dialysis techniques 7.7
17. Quantitative urine output measurement (e.g. by indwelling catheter) 7.0
NEUROLOGICAL SUPPORT
18. Measurement of intracranial pressure 1.6
METABOLIC SUPPORT
19. Treatment of complicated metabolic acidosis/alkalosis 1.3
20. Intravenous hyperalimentation 2.8
21. Enteral feeding through gastric tube or other gastrointestinal route 1.3
SPECIFIC INTERVENTIONS
22. Specific intervention in the ICU: endotracheal intubation, insertion of pacemaker, cardioversion, endoscopies, emergency surgery 2.8
in the previous 24 h, gastric lavage; routine interventions without direct consequences to the clinical condition of the patient
(e.g. X-ray, ECG, echo, dressings, insertion of CVC or arterial catheters) not included
23. Specific interventions outside the ICU; surgery or diagnostics procedures 1.9
TOTAL NURSE ACTIVITIES SCORE
89
a proxy measure of nursing workload in the ICU. One workload, staffing requirements and costing, and to dif-
91
of the primary uses was to aid quantitative comparison ferentiate between ICU and HDU patients. This simpli-
between patients in order to allocate resources, with fied version of 28 items is divided into basic activities
ongoing daily measurements giving an indication of (including monitoring and medications), ventilatory
patients’ progress. The original TISS had a number of support, cardio vascular support, renal support, neuro-
areas for scoring, including patient care and monitoring, logical support, metabolic support and specific
procedures, infusions and medications, and cardiopul- in terventions. The score range is from 1 to 8, with an
monary support. Points assigned to specific interventions ICU-type patient expected to score over 40 points. It
ranged from 1 to 4 for a 24-hour period. A higher score was estimated that a critical care nurse is able to provide
signified a greater therapeutic effort. Several revisions and 46 TISS-28 points per shift, with a score <10 signifying
variants of TISS have been developed in Europe, includ- a ward patient, 10–19 an HDU-type patient, and >20,
79
79
ing TISS-28 and the nine equivalents of nursing man- an HDU/ICU level. Most studies report mean daily
92
93
power (NEMS). 80,90 TISS scores (e.g. 23 [range 14–35], 36 [range 29–49]
94
and 21 [±12] ). Such diversity in scores reflects a
79
TISS-28 was refined to be a more user-friendly instru- range in acuity of patients. Total ICU admission TISS
ment, with similar precision to measure nursing scores are also occasionally reported. 95,96 Importantly,