Page 74 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 74
Quality and Safety 51
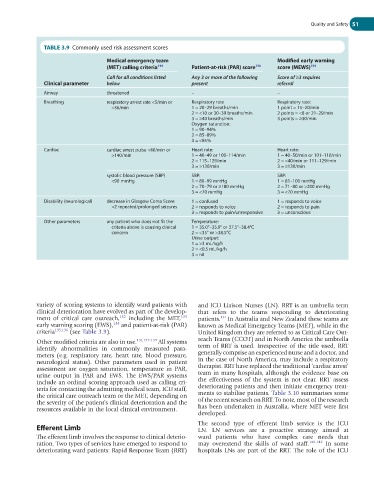
TABLE 3.9 Commonly used risk assessment scores
Medical emergency team Modified early warning
(MET) calling criteria 144 Patient-at-risk (PAR) score 136 score (MEWS) 134
Call for all conditions listed Any 3 or more of the following Score of ≥3 requires
Clinical parameter below present referral
Airway threatened – –
Breathing respiratory arrest rate <5/min or Respiratory rate Respiratory rate:
>36/min 1 = 20–29 breaths/min 1 point = 15–20/min
2 = <10 or 30–39 breaths/min 2 points = <8 or 21–29/min
3 = ≥40 breaths/min 3 points = ≥30/min
Oxygen saturation:
1 = 90–94%
2 = 85–89%
3 = <85%
Cardiac cardiac arrest pulse <40/min or Heart rate: Heart rate:
>140/min 1 = 40–49 or 100–114/min 1 = 40–50/min or 101–110/min
2 = 115–129/min 2 = <40/min or 111–129/min
3 = >130/min 3 = ≥130/min
systolic blood pressure (SBP) SBP: SBP:
<90 mmHg 1 = 80–99 mmHg 1 = 81–100 mmHg
2 = 70–79 or ≥180 mmHg 2 = 71–80 or >200 mmHg
3 = <70 mmHg 3 = <70 mmHg
Disability (neurological) decrease in Glasgow Coma Score 1 = confused 1 = responds to voice
>2 repeated/prolonged seizures 2 = responds to voice 2 = responds to pain
3 = responds to pain/unresponsive 3 = unconscious
Other parameters any patient who does not fit the Temperature:
criteria above is causing clinical 1 = 35.0°–35.9° or 37.5°–38.4°C
concern 2 = <35° or >38.5°C
Urine output:
1 = >3 mL/kg/h
2 = <0.5 mL/kg/h
3 = nil
variety of scoring systems to identify ward patients with and ICU Liaison Nurses (LN). RRT is an umbrella term
clinical deterioration have evolved as part of the develop- that refers to the teams responding to deteriorating
ment of critical care outreach, 132 including the MET, 133 patients. In Australia and New Zealand these teams are
131
early warning scoring (EWS), 134 and patient-at-risk (PAR) known as Medical Emergency Teams (MET), while in the
criteria 135,136 (see Table 3.9). United Kingdom they are referred to as Critical Care Out-
Other modified criteria are also in use. 131,137-139 All systems reach Teams (CCOT) and in North America the umbrella
identify abnormalities in commonly measured para- term of RRT is used. Irrespective of the title used, RRT
meters (e.g. respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure, generally comprise an experienced nurse and a doctor, and
neurological status). Other parameters used in patient in the case of North America, may include a respiratory
assessment are oxygen saturation, temperature in PAR, therapist. RRT have replaced the traditional ‘cardiac arrest’
urine output in PAR and EWS. The EWS/PAR systems team in many hospitals, although the evidence base on
include an ordinal scoring approach used as calling cri- the effectiveness of the system is not clear. RRT assess
teria for contacting the admitting medical team, ICU staff, deteriorating patients and then initiate emergency treat-
the critical care outreach team or the MET, depending on ments to stabilise patients. Table 3.10 summarises some
the severity of the patient’s clinical deterioration and the of the recent research on RRT. To note, most of the research
resources available in the local clinical environment. has been undertaken in Australia, where MET were first
developed.
The second type of efferent limb service is the ICU
Efferent Limb LN. LN services are a proactive strategy aimed at
The efferent limb involves the response to clinical deterio- ward patients who have complex care needs that
ration. Two types of services have emerged to respond to may overextend the skills of ward staff. 140-142 In some
deteriorating ward patients: Rapid Response Team (RRT) hospitals LNs are part of the RRT. The role of the ICU