Page 804 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 804
A P P E N D I X C N O R M A L V A L U E S 781
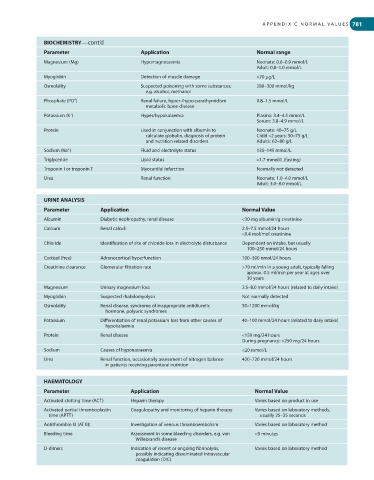
BIOCHEMISTRY—cont’d
Parameter Application Normal range
Magnesium (Mg) Hypomagnesaemia Neonate: 0.6–0.9 mmol/L
Adult: 0.8–1.0 mmol/L
Myoglobin Detection of muscle damage <70 μg/L
Osmolality Suspected poisoning with some substances, 280–300 mmol/kg
e.g. alcohol, methanol
Phosphate (PO ) 4 Renal failure, hyper-/hypo-parathyroidism 0.8–1.5 mmol/L
metabolic bone disease
+
Potassium (K ) Hyper/hypokalaemia Plasma: 3.4–4.5 mmol/L
Serum: 3.8–4.9 mmol/L
Protein Used in conjunction with albumin to Neonate: 40–75 g/L
calculate globulin, diagnosis of protein Child <2 years: 50–75 g/L
and nutrition related disorders Adults: 62–80 g/L
Sodium (Na ) Fluid and electrolyte status 135–145 mmol/L
+
Triglyceride Lipid status <1.7 mmol/L (fasting)
Troponin I or troponin T Myocardial infarction Normally not detected
Urea Renal function Neonate: 1.0–4.0 mmol/L
Adult: 3.0–8.0 mmol/L
URINE ANALYSIS
Parameter Application Normal Value
Albumin Diabetic nephropathy, renal disease <30 mg albumin/g creatinine
Calcium Renal calculi 2.5–7.5 mmol/24 hours
<0.4 mol/mol creatinine
Chloride Identification of site of chloride loss in electrolyte disturbance Dependent on intake, but usually
100–250 mmol/24 hours
Cortisol (free) Adrenocortical hyperfunction 100–300 nmol/24 hours
Creatinine clearance Glomerular filtration rate >70 ml/min in a young adult, typically falling
approx. 0.5 ml/min per year at ages over
30 years
Magnesium Urinary magnesium loss 2.5–8.0 mmol/24 hours (related to daily intake)
Myoglobin Suspected rhabdomyolysis Not normally detected
Osmolality Renal disease, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic 50–1200 mmol/kg
hormone, polyuric syndromes
Potassium Differentiation of renal potassium loss from other causes of 40–100 mmol/24 hours (related to daily intake)
hypokalaemia
Protein Renal disease <150 mg/24 hours
During pregnancy: <250 mg/24 hours
Sodium Causes of hyponatraemia <20 mmol/L
Urea Renal function, occasionally assessment of nitrogen balance 420–720 mmol/24 hours
in patients receiving parenteral nutrition
HAEMATOLOGY
Parameter Application Normal Value
Activated clotting time (ACT) Heparin therapy Varies based on product in use
Activated partial thromboplastin Coagulopathy and monitoring of heparin therapy Varies based on laboratory methods,
time (APTT) usually 25–35 seconds
Antithrombin III (AT III) Investigation of venous thromboembolism Varies based on laboratory method
Bleeding time Assessment in some bleeding disorders, e.g. von <9 minutes
Willebrand’s disease
D-dimers Indication of recent or ongoing fibrinolysis, Varies based on laboratory method
possibly indicating disseminated intravascular
coagulation (DIC)