Page 1213 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1213
Chapter 67 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia 1059
bone marrow biopsy, or the development of extramedullary blastic PROGNOSIS
infiltrates. In approximately two-thirds of patients, the blasts have a
myeloid or undifferentiated-like phenotype, whereas in the remaining A number of prognostic scoring systems have been developed with
third the blasts appear more lymphoid-like. Immunophenotypic the goal of predicting the length of CP in individual patients. The
analysis is recommended to characterize the nature of the blasts (Fig. best-known and most widely used index was developed by Sokal and
67.4). Extramedullary BC most commonly affects the skin, lymph colleagues. An algorithm was identified using spleen size, percentage
nodes, spleen, bone, or CNS, but it may occur elsewhere and may of circulating blasts, platelet count, and age as prognostic factors for
be of myeloid or lymphoid lineage. CP patients. However, the Sokal scale was based on therapies available
at that time (busulfan [BU], splenectomy), and newer systems for
patients treated with IFN subsequently resulted in newer prognostic
scoring systems. These scales, however, may have limited predictive
TABLE WHO Criteria for Accelerated and Blast Phases of value in the age of TKIs.
67.1 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Approximately 20% of patients with CML have deletions of
Accelerated Diagnosis can be made if one or more of the chromosomal material of varying size on the derivative 9q+. These
phase following is present: deletions presumably occur at the same time as the formation of the
Blasts 10% to 19% of peripheral blood white Ph chromosome, and are thus not considered to be additional clonal
cells or bone marrow cells changes as would be suggestive of AP disease. Patients with der 9q+
Peripheral blood basophils at least 20% have a worse prognosis if they receive IFN therapy; it is unclear
Persistent thrombocytopenia (<100 × 10 /L) whether or not such deletions have a poor prognosis in patients
9
unrelated to therapy, or persistent receiving imatinib therapy.
thrombocytosis (>1000 × 10 /L) Population-based studies investigating CML mortality in the
9
unresponsive to therapy imatinib era are now becoming available. They show that the pattern
Increasing spleen size and increasing WBC of mortality in CML patients related to high Sokal scores has become
count unresponsive to therapy similar to those of intermediate scores induced by the use of imatinib
Cytogenetic evidence of clonal evolution (i.e., in CP-CML patients. 4
the appearance of an additional genetic
abnormality that was not present in the
initial specimen at the time of diagnosis of THERAPY
CP CML)
Megakaryocytic proliferation in sizable sheets Definitions of Response to Treatment
and clusters, associated with marked
reticulin or collagen fibrosis, and/or severe Hematologic, cytogenetic, and molecular responses to treatment in
granulocytic dysplasia, should be considered CML have been defined (Table 67.2). A complete hematologic
as suggestive of AP CML. (These findings response (CHR) is defined as the achievement of normal WBC and
have not yet been analyzed in large clinical platelet counts and normal differential, along with the disappearance
studies; thus, it is not clear whether they are of all symptoms and signs of CML. A partial hematologic response
independent criteria for AP. They often occur is defined as a decrease in the WBC count to less than 50% of the
simultaneously with one or more of the other pretreatment level or the normalization of the WBC count accom-
features listed.) panied by persistent splenomegaly or immature cells in the peripheral
+
Blast crisis Diagnosis can be made if one or more of following blood. A CCR is defined as the absence of Ph metaphases in marrow
+
is present: cells, along with partial cytogenetic response as 1% to 34% Ph
Blasts 20% or more of peripheral WBCs or bone metaphases. Major cytogenetic remission (MCR) combines the per-
marrow cells centages of complete and partial response. There is now increasing
Extramedullary blast proliferation reliance on BCR-ABL mRNA levels for assessment of response.
Large foci or clusters of blasts in bone marrow According to the international scale for comparison of BCR-ABL
3
biopsy mRNA levels, a MMR is defined as a value of 0.1% or less. Lack of
detection of BCR-ABL mRNA is referred to as a complete molecular
AP, Accelerated phase; CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; CP, chronic phase; response (CMR). Since the ability to detect BCR-ABL mRNA
WBC, white blood cell.
depends on the sensitivity of the PCR assay, there is now consensus
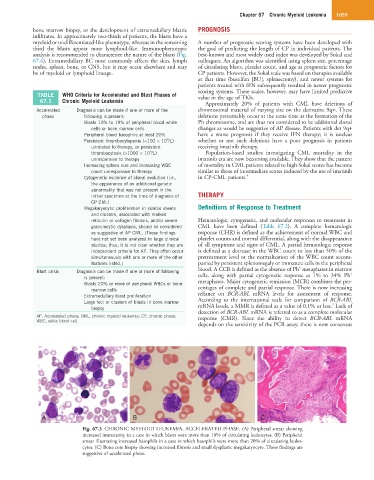
A B C
Fig. 67.3 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA, ACCELERATED PHASE. (A) Peripheral smear showing
increased immaturity in a case in which blasts were more than 10% of circulating leukocytes. (B) Peripheral
smear illustrating increased basophils in a case in which basophils were more than 20% of circulating leuko-
cytes. (C) Bone core biopsy showing increased fibrosis and small dysplastic megakaryocyte. These findings are
suggestive of accelerated phase.