Page 1216 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1216
1062 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
A B C
D E F
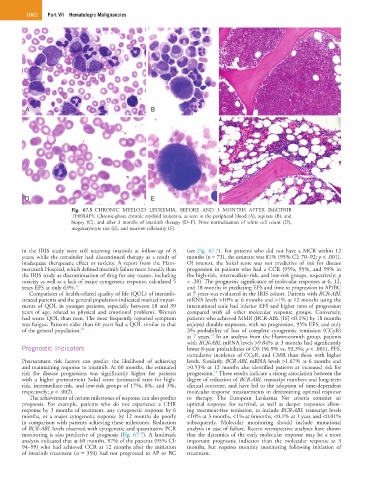
Fig. 67.5 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA, BEFORE AND 3 MONTHS AFTER IMATINIB
THERAPY. Chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia, as seen in the peripheral blood (A), aspirate (B), and
biopsy (C), and after 3 months of imatinib therapy (D–F). Note normalization of white cell count (D),
megakaryocyte size (E), and marrow cellularity (F).
in the IRIS study were still receiving imatinib at follow-up of 8 (see Fig. 67.7). For patients who did not have a MCR within 12
years, while the remainder had discontinued therapy as a result of months (n = 73), the estimate was 81% (95% CI: 70–92; p < .001).
inadequate therapeutic effect or toxicity. A report from the Ham- Of interest, the Sokal score was not predictive of risk for disease
mersmith Hospital, which defined imatinib failure more broadly than progression in patients who had a CCR (95%, 95%, and 99% in
the IRIS study as discontinuation of drug for any reason, including the high-risk, intermediate-risk, and low-risk groups, respectively; p
toxicity as well as a lack of major cytogenetic response, calculated 5 = .20). The prognostic significance of molecular responses at 6, 12,
years EFS at only 63%. 11 and 18 months in predicting EFS and time to progression to AP/BC
Comparison of health-related quality of life (QOL) of imatinib- at 7 years was evaluated in the IRIS cohort. Patients with BCR-ABL
treated patients and the general population indicated marked impair- mRNA levels >10% at 6 months and >1% at 12 months using the
ments of QOL in younger patients, especially between 18 and 39 international scale had inferior EFS and higher rates of progression
years of age, related to physical and emotional problems. Women compared with all other molecular response groups. Conversely,
had worse QOL than men. The most frequently reported symptom patients who achieved MMR (BCR-ABL [IS] <0.1%) by 18 months
was fatigue. Patients older than 60 years had a QOL similar to that enjoyed durable responses, with no progression, 95% EFS, and only
of the general population. 12 3% probability of loss of complete cytogenetic remission (CCyR)
13
at 7 years. In an analysis from the Hammersmith group, patients
with BCR-ABL mRNA levels >9.84% at 3 months had significantly
Prognostic Indicators lower 8-year probabilities of OS (56.9% vs. 93.3%; p < .001), PFS,
cumulative incidence of CCyR, and CMR than those with higher
Pretreatment risk factors can predict the likelihood of achieving levels. Similarly, BCR-ABL mRNA levels >1.67% at 6 months and
and maintaining response to imatinib. At 60 months, the estimated >0.53% at 12 months also identified patients at increased risk for
14
risk for disease progression was significantly higher for patients progression. These results indicate a strong association between the
with a higher pretreatment Sokal score (estimated rates for high- degree of reduction of BCR-ABL transcript numbers and long-term
risk, intermediate-risk, and low-risk groups of 17%, 8%, and 3%, clinical outcome, and have led to the adoption of time-dependent
respectively; p < .002). molecular response measurements in determining optimal response
The achievement of certain milestones of response can also predict to therapy. The European Leukemia Net criteria consider an
prognosis. For example, patients who do not experience a CHR optimal response for survival, as well as deeper responses allow-
response by 3 months of treatment, any cytogenetic response by 6 ing treatment-free remission, to include BCR-ABL transcript levels
months, or a major cytogenetic response by 12 months do poorly <10% at 3 months, <1% at 6months, <0.1% at 1 year, and <0.01%
in comparison with patients achieving these milestones. Reduction subsequently. Molecular monitoring should include mutational
of BCR-ABL levels observed with cytogenetic and quantitative PCR analysis in case of failure. Recent retrospective analyses have shown
monitoring is also predictive of prognosis (Fig. 67.7). A landmark that the dynamics of the early molecular response may be a more
analysis indicated that at 60 months, 97% of the patients (95% CI: important prognostic indicator than the molecular response at 3
94–99) who had achieved CCR at 12 months after the initiation months, but requires monthly monitoring following initiation of
of imatinib treatment (n = 350) had not progressed to AP or BC treatment.