Page 1214 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1214
1060 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
A B C
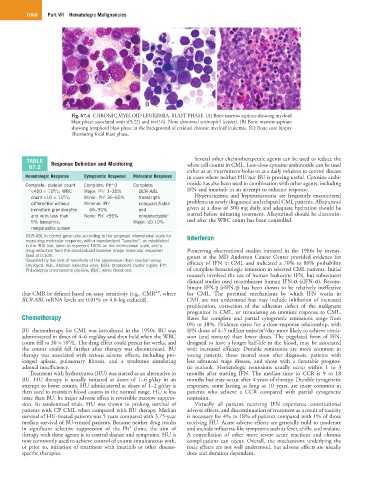
Fig. 67.4 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA, BLAST PHASE. (A) Bone marrow aspirate showing myeloid
blast phase associated with t(9;22) and inv(16). Note abnormal eosinophil (center). (B) Bone marrow aspirate
showing lymphoid blast phase in the background of residual chronic myeloid leukemia. (C) Bone core biopsy
illustrating focal blast phase.
TABLE Response Definition and Monitoring Several other chemotherapeutic agents can be used to reduce the
67.2 white cell counts in CML. Low-dose cytosine arabinoside can be used
either as an intermittent bolus or as a daily infusion to control disease
Hematologic Response Cytogenetic Response Molecular Response in cases where neither HU nor BU is proving useful. Cytosine arabi-
+
Complete: platelet count Complete: Ph 0 Complete: noside has also been used in combination with other agents, including
+
9
<450 × 10 /L; WBC Major: Ph 1–35% BCR-ABL IFN and imatinib in an attempt to enhance response.
9
count <10 × 10 /L; Minor: Ph 36–65% transcripts Hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria are frequently encountered
+
differential without Minimal: Ph nonquantifiable problems in newly diagnosed and relapsed CML patients. Allopurinol
+
immature granulocytes 66–95% and given at a dose of 300 mg daily and adequate hydration should be
+
and with less than None: Ph <95% nondetectable a started before initiating treatment. Allopurinol should be discontin-
5% basophils; Major: ≤0.10% ued after the WBC count has been controlled.
nonpalpable spleen
BCR-ABL to control gene ratio according to the proposed international scale for Interferon
measuring molecular response, with a standardized “baseline”, as established
in the IRIS trial, taken to represent 100% on the international scale, and a
3-log reduction from the standardized baseline (major molecular response) Pioneering observational studies initiated in the 1980s by investi-
fixed at 0.10%. gators at the MD Anderson Cancer Center provided evidence for
a Qualified by the limit of sensitivity of the polymerase chain reaction assay
+
employed. ABL, Abelson leukemia virus, BCR, breakpoint cluster region; Ph , efficacy of IFN in CML and indicated a 70% to 80% probability
Philadelphia chromosome positive; WBC, white blood cell. of complete hematologic remission in selected CML patients. Initial
research involved the use of human leukocyte IFN, but subsequent
clinical studies used recombinant human IFN-α (rIFN-α). Recom-
binant IFN-γ (rIFN-γ) has been shown to be relatively ineffective
4.0
that CMR be defined based on assay sensitivity (e.g., CMR , where for CML. The potential mechanisms by which IFN works in
BCR-ABL mRNA levels are 0.01% or 4.0-log reduced). CML are not understood but may include inhibition of increased
proliferation, correction of the adhesion defect of the malignant
progenitor in CML, or stimulating an immune response to CML.
Chemotherapy Rates for complete and partial cytogenetic remissions range from
0% to 38%. Evidence exists for a dose–response relationship, with
2
BU chemotherapy for CML was introduced in the 1950s. BU was IFN doses of 4–5 million units/m /day more likely to achieve remis-
administered in doses of 4–6 mg/day and then held when the WBC sion (and toxicity) than lower doses. The pegylated form of IFN,
9
count fell to 30 × 10 /L. The drug effect could persist for weeks, and designed to have a longer half-life in the blood, may be associated
the counts could fall further after therapy was discontinued. BU with increased efficacy. Durable remissions are more common in
therapy was associated with serious adverse effects, including pro- young patients, those treated soon after diagnosis, patients with
longed aplasia, pulmonary fibrosis, and a syndrome simulating less advanced stage disease, and those with a favorable prognos-
adrenal insufficiency. tic outlook. Hematologic remissions usually occur within 1 to 3
Treatment with hydroxyurea (HU) was started as an alternative to months after starting IFN. The median time to CCR is 9 to 18
BU. HU therapy is usually initiated at doses of 1–6 g/day in an months but may occur after 4 years of therapy. Durable cytogenetic
attempt to lower counts. HU administered at doses of 1–2 g/day is responses, some lasting as long as 10 years, are more common in
then used to maintain blood counts in the normal range. HU is less patients who achieve a CCR compared with partial cytogenetic
toxic than BU. Its major adverse effect is reversible marrow suppres- remission.
sion. In randomized trials, HU was shown to prolong survival of Virtually all patients receiving IFN experience constitutional
patients with CP CML when compared with BU therapy. Median adverse effects, and discontinuation of treatment as a result of toxicity
survival of HU-treated patients was 5 years compared with 3.75-year is necessary for 4% to 18% of patients compared with 1% of those
median survival of BU-treated patients. Because neither drug results receiving HU. Acute adverse effects are generally mild to moderate
+
in significant selective suppression of the Ph clone, the aim of and include influenza-like symptoms such as fever, chills, and malaise.
therapy with these agents is to control disease and symptoms. HU is A constellation of other more severe acute reactions and chronic
now commonly used to achieve control of counts simultaneous with, complications can occur. Overall, the mechanisms underlying the
or prior to, initiation of treatment with imatinib or other disease- toxic effects are not well understood, but adverse effects are usually
specific therapies. dose and duration dependent.