Page 1361 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1361
Chapter 74 Origin of Hodgkin Lymphoma 1207
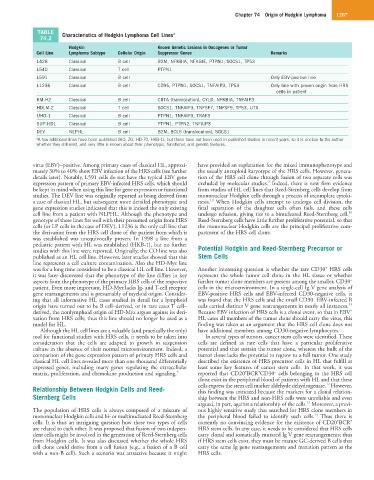
TABLE Characteristics of Hodgkin Lymphoma Cell Lines a
74.2
Hodgkin Known Genetic Lesions in Oncogenes or Tumor
Cell Line Lymphoma Subtype Cellular Origin Suppressor Genes Remarks
L428 Classical B cell B2M, NFKBIA, NFKBIE, PTPN1, SOCS1, TP53
L540 Classical T cell PTPN1
L591 Classical B cell Only EBV-positive line
L1236 Classical B cell CD95, PTPN1, SOCS1, TNFAIP3, TP53 Only line with proven origin from HRS
cells in patient
KM-H2 Classical B cell CIITA (translocation), CYLD, NFKBIA, TNFAIP3
HDLM-2 Classical T cell SOCS1, TNFAIP3, TNFSF7, TNFSF9, TP53, UTX
UHO-1 Classical B cell PTPN1, TNFAIP3, TRAF3
SUP-HD1 Classical B cell PTPN1, PTPN2, TNFAIP3
DEV NLPHL B cell B2M, BCL6 (translocation), SOCS1
a A few additional lines have been published (HO, ZO, HD-70, HKB-1), but these have not been used in published studies in recent years, so it is unclear to the author
whether they still exist, and very little is known about their phenotypic, functional, and genetic features.
virus (EBV)–positive. Among primary cases of classical HL, approxi- have provided an explanation for the mixed immunophenotype and
mately 30% to 40% show EBV infection of the HRS cells (see further the usually aneuploid karyotype of the HRS cells. However, genera-
details later). Notably, L591 cells do not have the typical EBV gene tion of the HRS cell clone through fusion of two separate cells was
9
expression pattern of primary EBV-infected HRS cells, which should excluded by molecular studies. Indeed, there is now firm evidence
be kept in mind when using this line for gene expression or functional from studies of HL cell lines that Reed-Sternberg cells develop from
studies. The DEV line was originally reported as being derived from mononuclear Hodgkin cells through a process of incomplete cytoki-
10
a case of classical HL, but subsequent more detailed phenotypic and nesis. When Hodgkin cells attempt to undergo cell division, the
gene expression studies indicated that this is indeed the only existing final separation of the daughter cells often fails, and these cells
10
cell line from a patient with NLPHL. Although the phenotype and undergo refusion, giving rise to a binucleated Reed-Sternberg cell.
genotype of these lines fits well with their presumed origin from HRS Reed-Sternberg cells have little further proliferative potential, so that
cells (or LP cells in the case of DEV), L1236 is the only cell line that the mononuclear Hodgkin cells are the principal proliferative com-
the derivation from the HRS cell clone of the patient from which it partment of the HRS cell clone.
was established was unequivocally proven. In 1998 a line from a
pediatric patient with HL was established (HKB-1), but no further
studies with this line were reported. Originally, the CO line was also Potential Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg Precursor or
published as an HL cell line. However, later studies showed that this Stem Cells
line represents a cell culture contamination. Also the HD-Myz line
+
was for a long time considered to be a classical HL cell line. However, Another interesting question is whether the rare CD30 HRS cells
it was later discovered that the phenotype of the line differs in key represent the whole tumor cell clone in the HL tissue or whether
–
aspects from the phenotype of the primary HRS cells of the respective further tumor clone members are present among the smaller, CD30
patient. Even more important, HD-Myz lacks Ig- and T-cell receptor cells in the microenvironment. In a single-cell Ig V gene analysis of
gene rearrangements and is presumably of myeloid origin. Consider- EBV-positive HRS cells and EBV-infected CD30-negative cells, it
–
ing that all informative HL cases studied in detail for a lymphoid was found that the HRS cells and the small CD30 EBV-infected B
11
origin have turned out to be B cell–derived, or in rare cases T cell– cells carried distinct V gene rearrangements in nearly all instances.
+
derived, the nonlymphoid origin of HD-Myz argues against its deri- Because EBV infection of HRS cells is a clonal event, so that in EBV
vation from HRS cells; thus this line should no longer be used as a HL cases all members of the tumor clone should carry the virus, this
model for HL. finding was taken as an argument that the HRS cell clone does not
Although the HL cell lines are a valuable (and practically the only) have additional members among CD30-negative lymphocytes.
tool for functional studies with HRS cells, it needs to be taken into In several types of tumors, cancer stem cells were identified. These
consideration that the cells are adapted to growth in suspension cells are defined as rare cells that have a particular proliferative
culture in the absence of their normal microenvironment. Indeed, a potential and that sustain the tumor clone, whereas the bulk of the
comparison of the gene expression pattern of primary HRS cells and tumor clone lacks the potential to regrow to a full tumor. One study
classical HL cell lines revealed more than one thousand differentially described the existence of HRS precursor cells in HL that fulfill at
expressed genes, including many genes regulating the extracellular least some key features of cancer stem cells. In that work, it was
+
+
–
matrix, proliferation, and chemokine production and signaling. 8 reported that CD20 BCR CD30 cells belonging to the HRS cell
clone exist in the peripheral blood of patients with HL and that these
12
Relationship Between Hodgkin Cells and Reed- cells express the stem cell marker aldehyde dehydrogenase. However,
this finding was criticized because the markers for a clonal relation-
Sternberg Cells ship between the HRS and non-HRS cells were unreliable and even
13
argued, in part, against a relationship of the cells. Moreover, a previ-
The population of HRS cells is always composed of a mixture of ous highly sensitive study that searched for HRS clone members in
14
mononuclear Hodgkin cells and bi- or multinucleated Reed-Sternberg the peripheral blood failed to identify such cells. Thus there is
+
+
cells. It is thus an intriguing question how these two types of cells currently no convincing evidence for the existence of CD20 BCR
are related to each other. It was proposed that fusion of two indepen- HRS stem cells. In any case, it needs to be considered that HRS cells
dent cells might be involved in the generation of Reed-Sternberg cells carry clonal and somatically mutated Ig V gene rearrangements; thus
from Hodgkin cells. It was also discussed whether the whole HRS if HRS stem cells exist, they must be mature GC-derived B cells that
cell clone could derive from a cell fusion (e.g., a fusion of a B cell carry the same Ig gene rearrangements and mutation pattern as the
with a non-B cell). Such a scenario was attractive because it might HRS cells.