Page 1356 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1356
1202 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
A B C D D
E CD45 CD30 CD15 PAX5 CD20 OCT2 BOB1
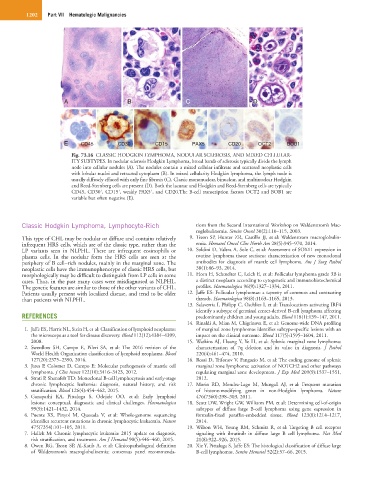
Fig. 73.16 CLASSIC HODGKIN LYMPHOMA, NODULAR SCLEROSIS, AND MIXED CELLULAR-
ITY SUBTYPES. In nodular sclerosis Hodgkin Lymphoma, broad bands of sclerosis typically divide the lymph
node into cellular nodules (A). The nodules contain a mixed cellular infiltrate and scattered neoplastic cells
with lobular nuclei and retracted cytoplasm (B). In mixed cellularity Hodgkin lymphoma, the lymph node is
usually diffusely effaced with only fine fibrosis (C). Classic mononuclear, binuclear, and multinuclear Hodgkin
and Reed-Sternberg cells are present (D). Both the lacunar and Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells are typically
+
+
+
CD45, CD30 , CD15 , weakly PAX5 , and CD20.The B-cell transcription factors OCT2 and BOB1 are
variable but often negative (E).
Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma, Lymphocyte-Rich tions from the Second International Workshop on Waldenstrom’s Mac-
roglobulinemia. Semin Oncol 30(2):110–115, 2003.
This type of CHL may be nodular or diffuse and contains relatively 9. Treon SP, Hunter ZR, Castillo JJ, et al: Waldenstrom macroglobulin-
infrequent HRS cells, which are of the classic type, rather than the emia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 28(5):945–970, 2014.
LP variants seen in NLPHL. There are infrequent eosinophils or 10. Soldini D, Valera A, Sole C, et al: Assessment of SOX11 expression in
plasma cells. In the nodular form the HRS cells are seen at the routine lymphoma tissue sections: characterization of new monoclonal
periphery of B cell–rich nodules, mainly in the marginal zone. The antibodies for diagnosis of mantle cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol
neoplastic cells have the immunophenotype of classic HRS cells, but 38(1):86–93, 2014.
morphologically may be difficult to distinguish from LP cells in some 11. Horn H, Schmelter C, Leich E, et al: Follicular lymphoma grade 3B is
cases. Thus, in the past many cases were misdiagnosed as NLPHL. a distinct neoplasm according to cytogenetic and immunohistochemical
The genetic features are similar to those of the other variants of CHL. profiles. Haematologica 96(9):1327–1334, 2011.
Patients usually present with localized disease, and tend to be older 12. Jaffe ES: Follicular lymphomas: a tapestry of common and contrasting
than patients with NLPHL. threads. Haematologica 98(8):1163–1165, 2013.
13. Salaverria I, Philipp C, Oschlies I, et al: Translocations activating IRF4
identify a subtype of germinal center-derived B-cell lymphoma affecting
REFERENCES predominantly children and young adults. Blood 118(1):139–147, 2011.
14. Rinaldi A, Mian M, Chigrinova E, et al: Genome-wide DNA profiling
1. Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, et al: Classification of lymphoid neoplasms: of marginal zone lymphomas identifies subtype-specific lesions with an
the microscope as a tool for disease discovery. Blood 112(12):4384–4399, impact on the clinical outcome. Blood 117(5):1595–1604, 2011.
2008. 15. Watkins AJ, Huang Y, Ye H, et al: Splenic marginal zone lymphoma:
2. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al: The 2016 revision of the characterization of 7q deletion and its value in diagnosis. J Pathol
World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 220(4):461–474, 2010.
127(20):2375–2390, 2016. 16. Rossi D, Trifonov V, Fangazio M, et al: The coding genome of splenic
3. Jares P, Colomer D, Campo E: Molecular pathogenesis of mantle cell marginal zone lymphoma: activation of NOTCH2 and other pathways
lymphoma. J Clin Invest 122(10):3416–3423, 2012. regulating marginal zone development. J Exp Med 209(9):1537–1551,
4. Strati P, Shanafelt TD: Monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis and early-stage 2012.
chronic lymphocytic leukemia: diagnosis, natural history, and risk 17. Morin RD, Mendez-Lago M, Mungall AJ, et al: Frequent mutation
stratification. Blood 126(4):454–462, 2015. of histone-modifying genes in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Nature
5. Ganapathi KA, Pittaluga S, Odejide OO, et al: Early lymphoid 476(7360):298–303, 2011.
lesions: conceptual, diagnostic and clinical challenges. Haematologica 18. Scott DW, Wright GW, Williams PM, et al: Determining cell-of-origin
99(9):1421–1432, 2014. subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using gene expression in
6. Puente XS, Pinyol M, Quesada V, et al: Whole-genome sequencing formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Blood 123(8):1214–1217,
identifies recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2014.
475(7354):101–105, 2011. 19. Wilson WH, Young RM, Schmitz R, et al: Targeting B cell receptor
7. Hallek M: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2015 update on diagnosis, signaling with ibrutinib in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat Med
risk stratification, and treatment. Am J Hematol 90(5):446–460, 2015. 21(8):922–926, 2015.
8. Owen RG, Treon SP, Al-Katib A, et al: Clinicopathological definition 20. Xie Y, Pittaluga S, Jaffe ES: The histological classification of diffuse large
of Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia: consensus panel recommenda- B-cell lymphomas. Semin Hematol 52(2):57–66, 2015.