Page 1455 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1455
Chapter 80 Clinical Manifestations, Staging, and Treatment of Follicular Lymphoma 1295
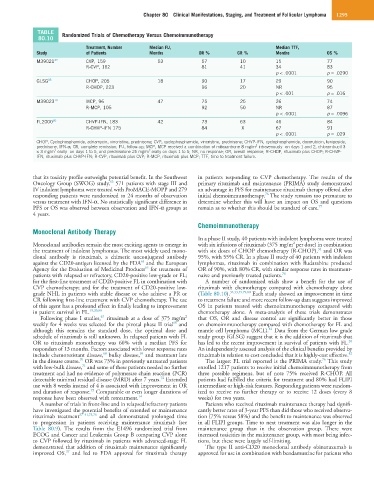
TABLE Randomized Trials of Chemotherapy Versus Chemoimmunotherapy
80.10
Treatment, Number Median FU, Median TTF,
Study of Patients Months OR % CR % Months OS %
M39021 32 CVP, 159 53 57 10 15 77
R-CVP, 162 81 41 34 83
p < .0001 p = .0290
GLSG 33 CHOP, 205 18 90 17 29 90
R-CHOP, 223 96 20 NR 95
p < .001 p = .016
M39023 79 MCP, 96 47 75 25 26 74
R-MCP, 105 92 50 NR 87
p < .0001 p = .0096
FL2000 80 CHVP-IFN, 183 42 73 63 46 84
R-CHVP-IFN 175 84 X 67 91
p < .0001 p = .029
CHOP, Cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, vincristine, prednisone; CVP, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone; CHVP-IFN, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, teniposide,
prednisone, IFN-α; CR, complete remission; FU, follow-up; MCP, MCP received a combination of mitoxantrone 8 mg/m intravenously on days 1 and 2, chlorambucil 3
2
2
2
× 3 mg/m orally on days 1 to 5, and prednisolone 25 mg/m orally on days 1 to 5; NR, no response; OR, overall response; R-CHOP, rituximab plus CHOP; R-CHVP-
IFN, rituximab plus CHVP-IFN; R-CVP, rituximab plus CVP; R-MCP, rituximab plus MCP; TTF, time to treatment failure.
that its toxicity profile outweighs potential benefit. In the Southwest in patients responding to CVP chemotherapy. The results of the
63
Oncology Group (SWOG) study, 571 patients with stage III and primary rituximab and maintenance (PRIMA) study demonstrated
IV indolent lymphoma were treated with ProMACE-MOPP and 279 an advantage in PFS for maintenance rituximab therapy offered after
76
responding patients were randomized to 24 months of observation initial chemoimmunotherapy. The study remains too premature to
versus treatment with IFN-α. No statistically significant difference in determine whether this will have an impact on OS and questions
PFS or OS was observed between observation and IFN-α groups at remain as to whether this should be standard of care. 77
4 years.
Chemoimmunotherapy
Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
In a phase II study, 40 patients with indolent lymphoma were treated
2
Monoclonal antibodies remain the most exciting agents to emerge in with six infusions of rituximab (375 mg/m per dose) in combination
34
the treatment of indolent lymphomas. The most widely used mono- with six doses of CHOP chemotherapy (R-CHOP), and OR was
clonal antibody is rituximab, a chimeric unconjugated antibody 95%, with 55% CR. In a phase II study of 40 patients with indolent
64
against the CD20-antigen licensed by the FDA and the European lymphomas, rituximab in combination with fludarabine produced
65
Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products for treatment of OR of 90%, with 80% CR, with similar response rates in treatment-
patients with relapsed or refractory, CD20-positive low-grade or FL; naive and previously treated patients. 78
for the first-line treatment of CD20-positive FL in combination with A number of randomized trials show a benefit for the use of
CVP chemotherapy; and for the treatment of CD20-positive low- rituximab with chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone
grade NHL in patients with stable disease or who achieve a PR or (Table 80.10). 32,33,39,79,80 Each study showed an improvement in time
CR following first-line treatment with CVP chemotherapy. The use to treatment failure and more recent follow-up data suggests improved
of this agent has a profound effect in finally leading to improvement OS in patients treated with chemoimmunotherapy compared with
in patient survival in FL. 19,20,66 chemotherapy alone. A meta-analysis of these trials demonstrates
2
67
Following phase I studies, rituximab at a dose of 375 mg/m that OS, OR and disease control are significantly better in those
68
weekly for 4 weeks was selected for the pivotal phase II trial and on chemoimmunotherapy compared with chemotherapy for FL and
81
although this remains the standard dose, the optimal dose and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Data from the German low grade
schedule of rituximab is still unknown. In relapsed patients with FL study group (GLSG) suggest that it is the addition of rituximab that
20
OR to rituximab monotherapy was 60% with a median PFS for has led to the recent improvement in survival of patients with FL.
responders of 13 months. Factors associated with lower response rates An independently assessed analysis of the clinical benefits provided by
68
69
include chemoresistant disease, bulky disease, and treatment late rituximab in relation to cost concluded that it is highly-cost effective. 82
70
76
in the disease course. OR was 73% in previously untreated patients The largest FL trial reported is the PRIMA study. This study
71
with low-bulk disease, and some of these patients needed no further enrolled 1217 patients to receive initial chemoimmunotherapy from
treatment and had no evidence of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) three possible regimens, but of note 75% received R-CHOP. All
72
detectable minimal residual disease (MRD) after 7 years. Extended patients had fulfilled the criteria for treatment and 80% had FLIPI
use with 8 weeks instead of 4 is associated with improvement in OR intermediate or high-risk features. Responding patients were random-
73
and duration of response. Comparable or even longer durations of ized to receive no further therapy or to receive 12 doses (every 8
response have been observed with retreatment. 74 weeks) for two years.
A number of trials in front-line and in relapsed/refractory patients Patients who received rituximab maintenance therapy had signifi-
have investigated the potential benefits of extended or maintenance cantly better rates of 3-year PFS than did those who received observa-
rituximab treatment 37–41,75,76 and all demonstrated prolonged time tion (75% versus 58%) and the benefit to maintenance was observed
to progression in patients receiving maintenance rituximab (see in all FLIPI groups. Time to next treatment was also longer in the
Table 80.9). The results from the E1496 randomized trial from maintenance group than in the observation group. There were
ECOG and Cancer and Leukemia Group B comparing CVP alone increased toxicities in the maintenance group, with most being infec-
to CVP followed by rituximab in patients with advanced-stage FL tions, but these were largely self-limiting.
demonstrated that addition of rituximab maintenance significantly The type II anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody obinutuzumab is
37
improved OS, and led to FDA approval for rituximab therapy approved for use in combination with bendamustine for patients who