Page 1477 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1477
1312 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
A 1.0 B 1.0
0.8 0.8
Proportion PFS 0.6 Proportion OS 0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.0
0.0 p .06 RR 2.0 (0.8–4.7) 0.2 p .12 RR 1.8 (0.7–4.8)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Time (years) Time (years)
C 1.0 D 1.0
0.8 0.8
Proportion PFS 0.6 Proportion OS 0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2 p .001 RR 3.6 (1.6–8.4) 0.2 p .01 RR 2.8 (1.1–7.3)
0.0 0.0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Time (years) Time (years)
E 1.0 F 1.0
0.8 0.8
Proportion PFS 0.6 Proportion OS 0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.0
0.0 p .01 RR 2.6 (1.1–6.3) 0.2 p .04 RR 2.3 (0.8–6.3)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Time (years) Time (years)
Germinal center B-cell–like DLBCL Unclassified DLBCL Activated B-cell–like DLBCL
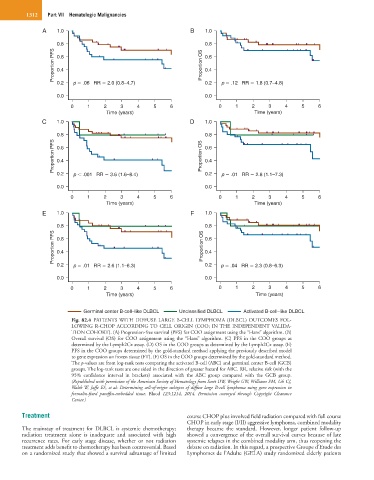
Fig. 82.4 PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE LARGE B-CELL LYMPHOMA (DLBCL) OUTCOMES FOL-
LOWING R-CHOP ACCORDING TO CELL ORIGIN (COO; IN THE INDEPENDENT VALIDA-
TION COHORT). (A) Progression-free survival (PFS) for COO assignment using the “Hans” algorithm. (B)
Overall survival (OS) for COO assignment using the “Hans” algorithm. (C) PFS in the COO groups as
determined by the Lymph2Cx assay. (D) OS in the COO groups as determined by the Lymph2Cx assay. (E)
PFS in the COO groups determined by the gold-standard method applying the previously described model
to gene expression on frozen tissue (FT). (F) OS in the COO groups determined by the gold-standard method.
The p-values are from log-rank tests comparing the activated B-cell (ABC) and germinal center B-cell (GCB)
groups. The log-rank tests are one sided in the direction of greater hazard for ABC. RR, relative risk (with the
95% confidence interval in brackets) associated with the ABC group compared with the GCB group.
(Republished with permission of the American Society of Hematology from Scott DW, Wright GW, Williams PM, Lih CJ,
Walsh W, Jaffe ES, et al: Determining cell-of-origin subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using gene expression in
formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Blood 123:1214, 2014. Permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance
Center.)
Treatment course CHOP plus involved field radiation compared with full course
CHOP in early stage (I/II) aggressive lymphoma, combined modality
The mainstay of treatment for DLBCL is systemic chemotherapy; therapy became the standard. However, longer patient follow-up
radiation treatment alone is inadequate and associated with high showed a convergence of the overall survival curves because of late
recurrence rates. For early stage disease, whether or not radiation systemic relapses in the combined modality arm, thus reopening the
treatment adds benefit to chemotherapy has been controversial. Based debate on radiation. In this regard, a prospective Groupe d’Etude des
on a randomized study that showed a survival advantage of limited Lymphomes de l’Adulte (GELA) study randomized elderly patients