Page 1479 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1479
1314 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
≤60 years and CHOP-14 benefited patients >60 years, these survival
gains did not remain significant with the addition of rituximab,
(following on from a GELA study that showed a survival advantage
in older patients treated with R-CHOP versus CHOP). The
RICOVER-60 study was a randomized comparison in elderly patients
of six versus eight cycles of CHOP-14, with or without rituximab.
Although the DSHNHL found no significant differences in survival
between the two groups, they reached the conclusion that R-CHOP-
14 should be adapted as the new standard based on historical com-
parisons in this population. Subsequently, however, two randomized
studies, one in all age groups (≥18 years) and the other in older
patients (>60 years), showed no benefit of R-CHOP-14 over
R-CHOP-21. 9,10 Therefore, R-CHOP-21 remains the standard.
Others have investigated the use of increased dose intensity
approaches as an alternative to R-CHOP. Rituximab with doxorubi-
cin, cyclophosphamide, vindesine, bleomycin, and prednisone
(R-ACVBP) was compared to R-CHOP-21 in a randomized study
performed by the GELA group in patients under 60 years with an
11
age-adjusted international prognostic index score of 1. While the
R-ACVBP arm showed an improved progression free-survival (PFS)
(87% versus 73%), the significant hematologic toxicity of the regimen
confines its use to younger patients and it is not feasible for most
patients with DLBCL who are over the age of 65 years. This restricts
the potential of approaches like R-ACVBP to replace R-CHOP as
the universal platform for this disease. Other intensive approaches
such as using autologous stem cell transplantation in the upfront
setting have been tried but they have never shown a clear benefit over
12
R-CHOP alone and are associated with much higher toxicity.
Another increased dose-intensity regimen is dose-adjusted etoposide,
prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin with
13
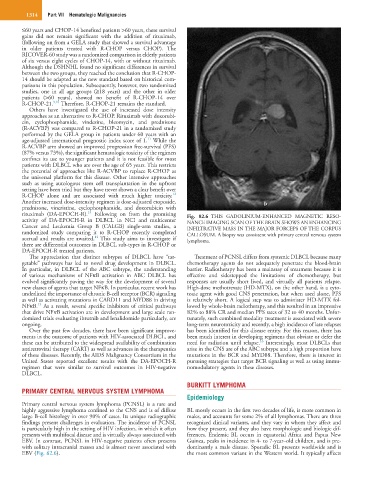
rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R). Following on from the promising Fig. 82.6 THIS GADOLINIUM-ENHANCED MAGNETIC RESO-
activity of DA-EPOCH-R in DLBCL in NCI and multicenter NANCE IMAGING SCAN OF THE BRAIN SHOWS AN ENHANCING
Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB) single-arm studies, a INFILTRATIVE MASS IN THE MAJOR FORCEPS OF THE CORPUS
randomized study comparing it to R-CHOP recently completed CALLOSUM. A biopsy was consistent with primary central nervous system
14
accrual and results are awaited. This study aims to investigate if lymphoma.
there are differential outcomes in DLBCL sub-types in R-CHOP or
DA-EPOCH-R treated patients.
The appreciation that distinct subtypes of DLBCL have “tar- Treatment of PCNSL differs from systemic DLBCL because many
getable” pathways has led to novel drug development in DLBCL. chemotherapy agents do not adequately penetrate the blood-brain
In particular, in DLBCL of the ABC subtype, the understanding barrier. Radiotherapy has been a mainstay of treatment because it is
of various mechanisms of NFκB activation in ABC DLBCL has effective and sidestepped the limitations of chemotherapy, but
evolved significantly paving the way for the development of several responses are usually short lived, and virtually all patients relapse.
new classes of agents that target NFκB. In particular, recent work has High-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX), on the other hand, is a cyto-
underlined the importance of chronic B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling toxic agent with good CNS penetration, but when used alone, PFS
as well as activating mutations in CARD11 and MYD88 in driving is relatively short. A logical step was to administer HD-MTX fol-
15
NFκB. As a result, several specific inhibitors of critical pathways lowed by whole-brain radiotherapy, and this resulted in an impressive
that drive NFκB activation are in development and large scale ran- 82% to 88% CR and median PFS rates of 32 to 40 months. Unfor-
domized trials evaluating ibrutnib and lenalidomide particularly, are tunately, such combined modality treatment is associated with severe
ongoing. long-term neurotoxicity and recently, a high incidence of late relapses
Over the past few decades, there have been significant improve- has been identified for this disease entity. For this reason, there has
ments in the outcome of patients with HIV-associated DLBCL, and been much interest in developing regimens that obviate or defer the
16
these can be attributed to the widespread availability of combination need for radiation until relapse. Interestingly, most DLBCLs that
antiretroviral therapy (CART) as well as advances in the therapeutics arise in the CNS are of the ABC subtype and a high proportion have
of these diseases. Recently, the AIDS Malignancy Consortium in the mutations in the BCR and MYD88. Therefore, there is interest in
United States reported excellent results with the DA-EPOCH-R pursuing strategies that target BCR signaling as well as using immu-
regimen that were similar to survival outcomes in HIV-negative nomodulatory agents in these diseases.
DLBCL.
BURKITT LYMPHOMA
PRIMARY CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM LYMPHOMA
Epidemiology
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) is a rare and
highly aggressive lymphoma confined to the CNS and is of diffuse BL mostly occurs in the first two decades of life, is more common in
large B-cell histology in over 90% of cases. Its unique radiographic males, and accounts for some 2% of all lymphomas. There are three
findings present challenges in evaluation. The incidence of PCNSL recognized clinical variants, and they vary in whom they affect and
is particularly high in the setting of HIV infection, in which it often how they present, and they also have morphologic and biologic dif-
presents with multifocal disease and is virtually always associated with ferences. Endemic BL occurs in equatorial Africa and Papua New
EBV. In contrast, PCNSL in HIV-negative patients often presents Guinea, peaks in incidence in 4- to 7-year–old children, and is pre-
with solitary intracranial masses and is almost never associated with dominantly a male disease. Sporadic BL presents worldwide and is
EBV (Fig. 82.6). the most common variant in the Western world. It typically affects