Page 1556 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1556
Chapter 86 Plasma Cell Neoplasms 1383
60
Both sexes
50 Male
Female
Incidence per 100,000 30
40
20
10
0
25-29 30-34 35-39 40-44 45-49 50-54 55-59 60-64 65-69 70-74 75-79 80-84 85+
A Age (yr)
20
Male incidence
Male mortality
Female incidence
Incidence per 100,000 10
15
Female mortality
5
0
All races White African Asian and American Hispanic
American Pacific Islander Indian
B Race
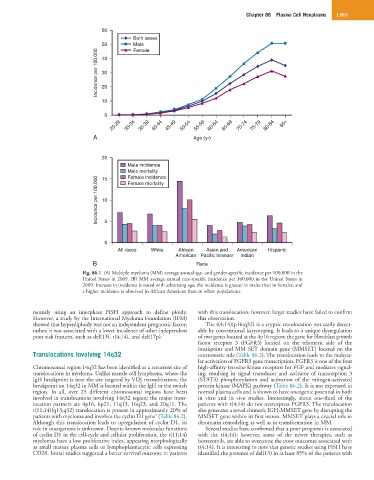
Fig. 86.1 (A) Multiple myeloma (MM) average annual age- and gender-specific incidence per 100,000 in the
United States in 2009. (B) MM average annual race-specific incidence per 100,000 in the United States in
2009. Increase in incidence is noted with advancing age; the incidence is greater in males than in females; and
a higher incidence is observed in African American than in white populations.
recently using an interphase FISH approach to define ploidy. with this translocation; however, larger studies have failed to confirm
However, a study by the International Myeloma Foundation (IFM) this observation.
showed that hyperdiploidy was not an independent prognostic factor; The t(4;14)(p16;q32) is a cryptic translocation not easily detect-
rather, it was associated with a lower incidence of other independent able by conventional karyotyping. It leads to a unique dysregulation
poor risk features, such as del(13), t(4;14), and del(17p). 3 of two genes located at the 4p16 region; the gene for fibroblast growth
factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) located on the telomeric side of the
breakpoint and MM SET domain gene (MMSET) located on the
Translocations Involving 14q32 centromeric side (Table 86.2). The translocation leads to the molecu-
lar activation of FGFR3 gene transcription. FGFR3 is one of the four
Chromosomal region 14q32 has been identified as a recurrent site of high-affinity tyrosine kinase receptors for FGF and mediates signal-
translocations in myeloma. Unlike mantle cell lymphoma, where the ing, resulting in signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
IgH breakpoint is near the site targeted by VDJ recombination, the (STAT3) phosphorylation and activation of the mitogen-activated
breakpoint on 14q32 in MM is located within the IgH or the switch protein kinase (MAPK) pathway (Table 86.2). It is not expressed in
region. In all, over 25 different chromosomal regions have been normal plasma cells and is shown to have oncogenic potential in both
involved in translocations involving 14q32 region; the major trans- in vitro and in vivo studies. Interestingly, about one-third of the
location partners are 4p16, 6p21, 11q13, 16q23, and 20q11. The patients with t(4;14) do not overexpress FGFR3. The translocation
t(11;14)(q13;q32) translocation is present in approximately 20% of also generates a novel chimeric IGH-MMSET gene by disrupting the
4
patients with myeloma and involves the cyclin D1 gene (Table 86.2). MMSET gene within its first intron. MMSET plays a crucial role in
Although this translocation leads to upregulation of cyclin D1, its chromatin remodeling as well as in transformation in MM.
role in oncogenesis is unknown. Despite known molecular functions Several studies have confirmed that a poor prognosis is associated
of cyclin D1 in the cell-cycle and cellular proliferation, the t(11;14) with the t(4;14); however, some of the newer therapies, such as
myelomas have a low proliferative index, appearing morphologically bortezomib, are able to overcome the poor outcomes associated with
as small mature plasma cells or lymphoplasmacytic cells expressing t(4;14). It is interesting to note that genetic studies using FISH have
CD20. Initial studies suggested a better survival outcome in patients identified the presence of del(13) in at least 85% of the patients with