Page 1561 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1561
1388 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
MM
GSK-3β
Migration
FKHR
CD40 PKC Caspase-9 Survival
Antiapoptosis
NF-κB
Cell surface Akt mTOR Cell cycle
targets FGFR3 PI3K Bad
CS1 Bcl-xL Survival
JAK/STAT3
Mcl-1 Antiapoptosis
BAFF-R
Bcl-xL Survival
VEGFR NFκB IAP Anti-apoptosis
Cyclin-D Cell cycle
Cytokines Ras/Raf
IL-6, VEGF
IGF-1, SDF-1α, TNF-α MEK/ERK Proliferation
Kip1
BAFF, APRIL, TGFβ p27 Antiapoptosis
BSF-3 VEGF
Adhesion
Smad, ERK
Cytokines↑ NF-κB Adhesion
molecules↑
LFA-1
ICAM-1
MUC-1
BMSC
VCAM-1 VLA-4
Fibronectin
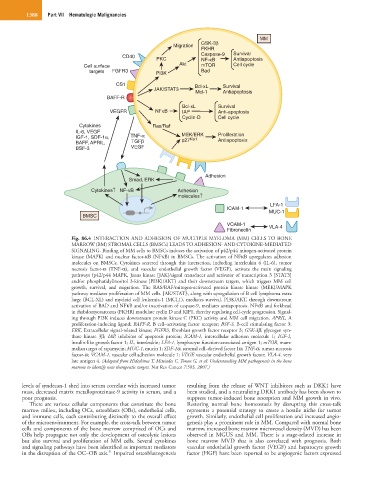
Fig. 86.4 INTERACTION AND ADHESION OF MULTIPLE MYELOMA (MM) CELLS TO BONE
MARROW (BM) STROMAL CELLS (BMSCs) LEADS TO ADHESION- AND CYTOKINE-MEDIATED
SIGNALING. Binding of MM cells to BMSCs induces the activation of p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein
kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor-κB (NFκB) in BMSCs. The activation of NFκB upregulates adhesion
molecules on BMSCs. Cytokines secreted through this interaction, including interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumor
necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), activate the main signaling
pathways (p42/p44 MAPK, Janus kinase [JAK]/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 [STAT3]
and/or phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase [PI3K]/AKT) and their downstream targets, which triggers MM cell
growth, survival, and migration. The RAS/RAF/mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)/MAPK
pathway mediates proliferation of MM cells. JAK/STAT3, along with upregulation of B cell lymphoma extra
large (BCL-XL) and myeloid cell leukemia-1 (MCL1), mediates survival. PI3K/AKT, through downstream
activation of BAD and NFκB and/or inactivation of caspase-9, mediates antiapoptosis. NFκB and forkhead
in rhabdomyosarcoma (FKHR) modulate cyclin D and KIP1, thereby regulating cell-cycle progression. Signal-
ing through PI3K induces downstream protein kinase C (PKC) activity and MM cell migration. APRIL, A
proliferation-inducing ligand; BAFF-R, B cell–activating factor receptor; BSF-3, B-cell stimulating factor 3;
ERK, Extracellular signal-related kinase; FGFR3, fibroblast growth factor receptor 3; GSK-3β, glycogen syn-
thase kinase 3β; IAP, inhibitor of apoptosis protein; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IGF-1,
insulin-like growth factor 1; IL, interleukin; LFA-1, lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1; mTOR, mam-
malian target of rapamycin; MUC-1, mucin 1; SDF-1α, stromal cell–derived factor 1α; TNF-α, tumor-necrosis
factor-α; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VLA-4, very
late antigen 4. (Adapted from Hideshima T, Mitsiades C, Tonon G, et al: Understanding MM pathogenesis in the bone
marrow to identify new therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer 7:585, 2007.)
levels of syndecan-1 shed into serum correlate with increased tumor resulting from the release of WNT inhibitors such as DKK1 have
mass, decreased matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in serum, and a been studied, and a neutralizing DKK1 antibody has been shown to
poor prognosis. suppress tumor-induced bone resorption and MM growth in vivo.
There are various cellular components that constitute the bone Restoring normal bone homeostasis by disrupting this cross-talk
marrow milieu, including OCs, osteoblasts (OBs), endothelial cells, represents a potential strategy to create a hostile niche for tumor
and immune cells, each contributing distinctly to the overall effect growth. Similarly, endothelial cell proliferation and increased angio-
of the microenvironment. For example, the cross-talk between tumor genesis play a prominent role in MM. Compared with normal bone
cells and components of the bone marrow comprised of OCs and marrow, increased bone marrow microvessel density (MVD) has been
OBs help propagate not only the development of osteolytic lesions observed in MGUS and MM. There is a stage-related increase in
but also survival and proliferation of MM cells. Several cytokines bone marrow MVD that is also correlated with prognosis. Both
and signaling pathways have been identified as important mediators vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hepatocyte growth
11
in the disruption of the OC–OB axis. Impaired osteoblastogenesis factor (HGF) have been reported to be angiogenic factors expressed