Page 1595 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1595
Chapter 87 Waldenström Macroglobulinemia/Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma 1421
is of significance, given its role as an adaptor molecule in Toll-like
44
receptor (TLR) and interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) signaling. All IMPACT OF WM GENOMICS ON
TLRs except for TLR3 use MYD88 to facilitate their signaling. CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Following TLR or IL-1R stimulation, MYD88 is recruited to the
activated receptor complex as a homodimer, which then complexes The importance of MYD88 and CXCR4 mutations in the clinical
with interleukin receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) and activates presentation of patients with WM was recently reported. Significantly
IRAK1 and IRAK2. 45–47 Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated higher BM involvement, serum IgM levels, and symptomatic disease
factor 6 is then activated by IRAK1, leading to NFκB activation via requiring therapy, including hyperviscosity syndrome, were observed
50
48
IκBα phosphorylation. Use of inhibitors of the MYD88 pathway in those patients with MYD88 L265P CXCR4 WHIM/NS mutations.
WT
led to decreased IRAK1 and IκBα phosphorylation, as well as to Patients with MYD88 L265P CXCR4 WHIM/FS or MYD88 L265P CXCR4
survival of MYD88 L265P -expressing WM cells. These observations are had intermediate BM and serum IgM levels; those with MYD-
WT
WT
of particular relevance to WM because NFκB signaling is important 88 CXCR4 showed the lowest BM disease burden. Fewer patients
49
for WM growth and survival. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) is also with MYD88 L265P and CXCR4 WHIM/FS or NS than with MYD88 L265P CX-
WT
. Activated BTK coimmunoprecipitates
activated by MYD88 L265P 43 CR4 presented with adenopathy, further delineating differences in
with MYD88, which could be abrogated by use of a BTK inhibitor, disease tropism based on CXCR4 status. Despite the more aggressive
and overexpression of MYD88 L265P but not WT MYD88 triggers presentation associated with CXCR4 WHIM/NS genotype, risk of death
BTK activation. Knockdown of MYD88 by lentiviral transfection or was not impacted by CXCR4 mutation status. Risk of death was
WT
use of a MYD88 homodimerization inhibitor also abrogated BTK found to be 10-fold higher in patients with the MYD88 versus the
activation in MYD88 L265P -mutated WM cells. MYD88 L265P genotype. 50
CXCR4 WHIM MUTATIONS MARROW MICROENVIRONMENT
The second most common somatic mutation after MYD88 L265P In patients with WM, increased numbers of mast cells are found in
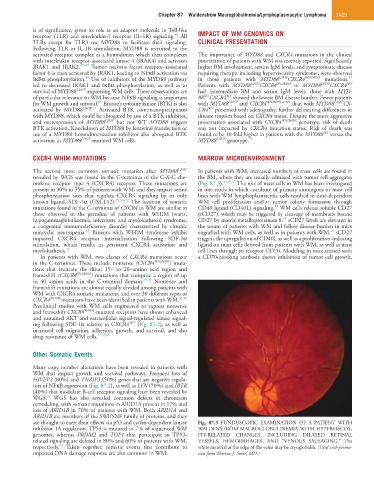
revealed by WGS was found in the C-terminus of the C-X-C che- the BM, where they are usually admixed with tumor cell aggregates
mokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) receptor. These mutations are (Fig. 87.3). 14,18,57 The role of mast cells in WM has been investigated
present in 30% to 35% of patients with WM, and they impact serine in one study in which coculture of primary autologous or mast cell
phosphorylation sites that regulate CXCR4 signaling by its only lines with WM lymphoplasmacytic cells resulted in dose-dependent
known ligand, SDF-1α (CXCL12). 29,50–52 The location of somatic WM cell proliferation and/or tumor colony formation through
57
mutations found in the C-terminus of CXCR4 in WM are similar to CD40 ligand (CD40L) signaling. WM cells release soluble CD27
those observed in the germline of patients with WHIM (warts, (sCD27), which may be triggered by cleavage of membrane bound
58
hypogammaglobulinemia, infections, and myelokathexis) syndrome, CD27 by matrix metalloproteinase 8. sCD27 levels are elevated in
a congenital immunodeficiency disorder characterized by chronic the serum of patients with WM and follow disease burden in mice
53
59
noncyclic neutropenia. Patients with WHIM syndrome exhibit engrafted with WM cells, as well as in patients with WM. sCD27
impaired CXCR4 receptor internalization following SDF-1α triggers the upregulation of CD40L as well as a proliferation-inducing
stimulation, which results in persistent CXCR4 activation and ligand on mast cells derived from patients with WM, as well as mast
myelokathexis. 54 cell lines through its receptor CD70. Modeling in mice treated with
In patients with WM, two classes of CXCR4 mutations occur a CD70-blocking antibody shows inhibition of tumor cell growth,
in the C-terminus. These include nonsense (CXCR4 WHIM/NS ) muta-
tions that truncate the distal 15– to 20–amino acid region and
frameshift (CXCR4 WHIM/FS ) mutations that comprise a region of up
to 40 amino acids in the C-terminal domain. 29,50 Nonsense and
frameshift mutations are almost equally divided among patients with
WM with CXCR4 somatic mutations, and over 30 different types of
CXCR4 WHIM mutations have been identified in patients with WM. 29,50
Preclinical studies with WM cells engineered to express nonsense
and frameshift CXCR4 WHIM -mutated receptors have shown enhanced
and sustained AKT and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signal-
WT
ing following SDF-1α relative to CXCR4 (Fig. 87.2), as well as
increased cell migration, adhesion, growth, and survival, and also
drug resistance of WM cells. 51,55,56
Other Somatic Events
Many copy number alterations have been revealed in patients with
WM that impact growth and survival pathways. Frequent loss of
HIVEP2 (80%) and TNAIP3 (50%) genes that are negative regula-
tors of NFκB expression (Fig. 87.2), as well as LYN (70%) and IBTK
(40%) that modulate B-cell receptor signaling have been revealed by
29
WGS. WGS has also revealed common defects in chromatin
remodeling, with somatic mutations in ARID1A present in 17% and
loss of ARID1B in 70% of patients with WM. Both ARID1A and
ARID1B are members of the SWI/SNF family of proteins, and they
are thought to exert their effects via p53 and cyclin-dependent kinase Fig. 87.3 FUNDUSCOPIC EXAMINATION OF A PATIENT WITH
inhibitor 1A regulation. TP53 is mutated in 7% of sequenced WM WALDENSTRÖM MACROGLOBULINEMIA WITH HYPERVISCOS-
genomes, whereas PRDM2 and TOP1 that participate in TP53- ITY-RELATED CHANGES, INCLUDING DILATED RETINAL
related signaling are deleted in 80% and 60% of patients with WM, VESSELS, HEMORRHAGES, AND “VENOUS SAUSAGING.” The
29
respectively. Taken together, somatic events that contribute to white material at the edge of the veins may be cryoglobulin. (Used with permis-
impaired DNA damage response are also common in WM. sion from Marvin J. Stone, MD.)