Page 171 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 171
Chapter 12 Cell Adhesion 129
The application of tension to integrins can increase ligand binding, protein leukocyte function-associated antigen-3 (LFA-3) and B7-1
and a reduction in tension lessens integrin adhesiveness. Cell–cell (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86), respectively, on antigen-presenting cells.
interactions result from integrin recognition of cell-surface members The immunoglobulin-like receptor, platelet and endothelial cell
of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Binding of fibrinogen to αIIbβ3 adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1; CD31) uses homotypical interac-
integrins on adjacent platelets creates a molecular bridge that promotes tions to promote contacts between adjacent endothelial cells and
platelet aggregation. Furthermore, fibrinogen simultaneously binds to to mediate adhesion of leukocytes to platelets and endothelium.
the αMβ2 integrin on leukocytes and to an immunoglobulin-like The immunoglobulin-like junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs),
receptor on endothelial cells, promoting leukocyte adhesion to the expressed on endothelial and epithelial cells and leukocytes, regulate
endothelium. endothelial and epithelial cell junctions, paracellular permeability,
and leukocyte trafficking between endothelial and epithelial cells
by homotypical interactions or by heterotypical interactions with
IMMUNOGLOBULIN-LIKE RECEPTORS integrins. JAM-A, the founding member of this family, functions as a
homodimer and transmits intracellular signals critical for its function
Immunoglobulin superfamily members contain a variable number of in regulation of endothelial and epithelial permeability.
disulfide-stabilized motifs similar to those in antibodies, which are
linked to transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains (Table 12.2; see
also Fig. 12.1). The immunoglobulin-like motif provides a frame- OTHER ADHESION RECEPTORS THAT MEDIATE
work on which specific recognition structures for other proteins can PROTEIN–PROTEIN INTERACTIONS
be added. Some of these motifs also recognize glycoconjugates. The
immunoglobulin-like molecules, intercellular adhesion molecule 1 Cadherins are cytoskeletally linked type 1 transmembrane proteins
and 2 (ICAM-1 and ICAM-2), and vascular cell adhesion molecule that mediate cell–cell contact in many organs through homotypical
1 (VCAM-1), expressed on endothelial cells, as well as ICAM-3, binding to cadherins on adjacent cells (Table 12.3). Cadherins have
expressed on leukocytes, mediate cell–cell contact through recog- not been described on blood cells but are found on endothelial
nition of specific integrins on leukocytes. ICAM-4, expressed on cells, where, similar to PECAM-1 and JAMs, they help form cell
erythroid precursors, binds to integrins on stromal cells of BM, junctions and participate in the process of leukocyte migration across
which may regulate erythropoiesis. ICAM-5 is restricted to neural endothelial cell-to-cell borders, termed diapedesis or transendothelial
tissues. The immunoglobulin-like GPVI on platelets promotes cell migration. Cadherins are also expressed in the epithelium and help
activation by binding to collagen exposed on damaged blood vessels. form cell-to-cell junctions.
Interactions between immunoglobulin-like molecules help to mediate The GPIb–IX–V complex on platelets consists of leucine-rich
adhesion between T cells and antigen-presenting cells. Thus, whereas protein subunits (see Fig. 12.1). Under conditions of high shear stress
the immunoglobulin-like molecules CD8 and CD4 on T cells bind such as those found in arterial circulation, this complex promotes the
to the conserved membrane-proximal domains of class I and class II initial platelet adhesion to injured vessels by binding to vWF exposed
major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins, respectively, the in the subendothelium. It also may assist interactions with other
α- and β-chains of the T-cell receptor (TCR) bind to the polymorphic platelets or with endothelial cells by binding to P-selectin, which
antigen-presenting domain. In addition, the immunoglobulin-like normally binds to glycoconjugates, and it may assist platelet adhesion
proteins CD2 and CD28 on T cells bind to the immunoglobulin-like to leukocytes by binding to the integrin α m β 2 .
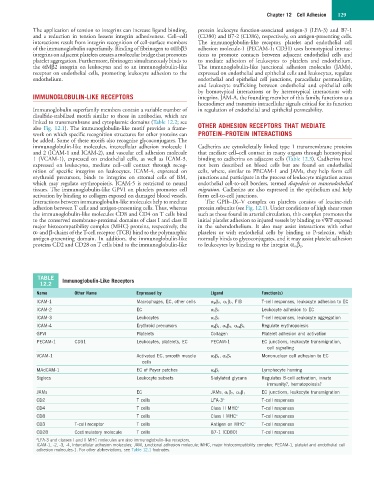
TABLE Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors
12.2
Name Other Name Expressed by Ligand Function(s)
ICAM-1 Macrophages, EC, other cells α M β 2 , α L β 2 , FIB T-cell responses, leukocyte adhesion to EC
ICAM-2 EC α L β 2 Leukocyte adhesion to EC
ICAM-3 Leukocytes α L β 2 T-cell responses, leukocyte aggregation
ICAM-4 Erythroid precursors α 4 β 1 , α V β 3 , α llb β 3 Regulate erythropoiesis
GPVI Platelets Collagen Platelet adhesion and activation
PECAM-1 CD31 Leukocytes, platelets, EC PECAM-1 EC junctions, leukocyte transmigration,
cell signaling
VCAM-1 Activated EC, smooth muscle α 4 β 1 , α 4 β 7 Mononuclear cell adhesion to EC
cells
MAdCAM-1 EC of Peyer patches α 4 β 7 Lymphocyte homing
Siglecs Leukocyte subsets Sialylated glycans Regulates B-cell activation, innate
immunity?, hematopoiesis?
JAMs EC JAMs, α L β 2 , α 4 β 1 EC junctions, leukocyte transmigration
CD2 T cells LFA-3 a T-cell responses
CD4 T cells Class II MHC a T-cell responses
CD8 T cells Class I MHC a T-cell responses
CD3 T-cell receptor T cells Antigen on MHC a T-cell responses
CD28 Costimulatory molecule T cells B7-1 (CD80) T-cell responses
a LFA-3 and classes I and II MHC molecules are also immunoglobulin-like receptors.
ICAM-1, -2, -3, -4, Intercellular adhesion molecules; JAM, junctional adhesion molecule; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; PECAM-1, platelet and endothelial cell
adhesion molecules-1. For other abbreviations, see Table 12.1 footnotes.