Page 1838 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1838
1634 Part X Transplantation
80
70 No graft (n = 26)
CB (n = 90)
60 URD (n = 296)
50
Patients, n 40
30
20
10
0
NW European Southern European European mix Asian African White Hispanic Middle Eastern
Non-European mix
Eastern European
Patient Ancestry
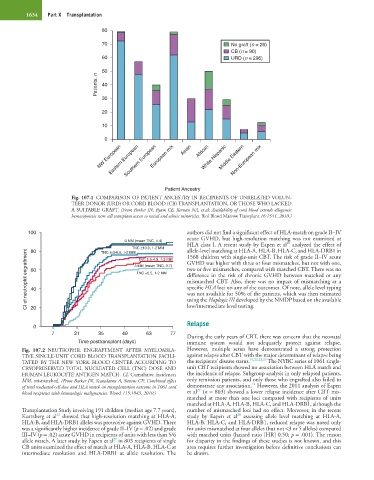
Fig. 107.1 COMPARISON OF PATIENT ANCESTRY IN RECIPIENTS OF UNRELATED VOLUN-
TEER DONOR (URD) OR CORD BLOOD (CB) TRANSPLANTATION, OR THOSE WHO LACKED
A SUITABLE GRAFT. (From Barker JN, Byam CE, Kernan NA, et al: Availability of cord blood extends allogeneic
hematopoietic stem cell transplant access to racial and ethnic minorities. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 16:1541, 2010.)
100 authors did not find a significant effect of HLA-match on grade II–IV
acute GVHD, but high-resolution matching was not examined at
0 MM (mean TNC, 4.4) 28
HLA class I. A recent study by Eapen et al analyzed the effect of
TNC ≥10.0, 1-2 MM allele-level matching at HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, and HLA-DRB1 in
80
CI of neutrophil engraftment 60 3 MM (mean TNC, 3.7) two or five mismatches, compared with matched CBT. There was no
TNC 5.0-9.9, 1-2 MM
1568 children with single-unit CBT. The risk of grade II–IV acute
TNC 2.5-4.9, 1-2 MM
GVHD was higher with three or four mismatches, but not with one,
TNC <2.5, 1-2 MM
difference in the risk of chronic GVHD between matched or any
mismatched CBT. Also, there was no impact of mismatching at a
specific HLA loci on any of the outcomes. Of note, allele level typing
40
was not available for 50% of the patients, which was then estimated
using the Haplogic III developed by the NMDP based on the available
low/intermediate level testing.
20
Relapse
0
7 21 35 49 63 77
During the early years of CBT, there was concern that the neonatal
Time posttransplant (days) immune system would not adequately protect against relapse.
Fig. 107.2 NEUTROPHIL ENGRAFTMENT AFTER MYELOABLA- However, multiple series have demonstrated a strong protection
TIVE SINGLE-UNIT CORD BLOOD TRANSPLANTATION FACILI- against relapse after CBT with the major determinant of relapse being
19,22,23,29
TATED BY THE NEW YORK BLOOD CENTER ACCORDING TO the recipients’ disease status. The NYBC series of 1061 single-
CRYOPRESERVED TOTAL NUCLEATED CELL (TNC) DOSE AND unit CBT recipients showed no association between HLA match and
HUMAN LEUKOCYTE ANTIGEN MATCH. CI, Cumulative incidence; the incidence of relapse. Subgroup analysis in only relapsed patients,
MM, mismatched. (From Barker JN, Scaradavou A, Stevens CE: Combined effect only remission patients, and only those who engrafted also failed to
12
of total nucleated cell dose and HLA match on transplantation outcome in 1061 cord demonstrate any association. However, the 2011 analysis of Eapen
27
blood recipients with hematologic malignancies. Blood 115:1843, 2010.) et al (n = 803) showed a lower relapse incidence after CBT mis-
matched at more than one loci compared with recipients of units
matched at HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, and HLA-DRB1, although the
Transplantation Study involving 191 children (median age 7.7 years), number of mismatched loci had no effect. Moreover, in the recent
28
23
Kurtzberg et al showed that high-resolution matching at HLA-A, study by Eapen et al assessing allele level matching at HLA-A,
HLA-B, and HLA-DRB1 alleles was protective against GVHD. There HLA-B, HLA-C, and HLA-DRB1, reduced relapse was noted only
was a significantly higher incidence of grade II–IV (p = .02) and grade for units mismatched at four alleles (but not <3 or 5 alleles) compared
III–IV (p = .02) acute GVHD in recipients of units with less than 5/6 with matched units (hazard ratio [HR] 0.50; p = .001). The reason
27
allele match. A later study by Eapen et al in 803 recipients of single for disparity in the findings of these studies is not known, and this
CB units examined the effect of match at HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C at area requires further investigation before definitive conclusions can
intermediate resolution and HLA-DRB1 at allele resolution. The be drawn.