Page 1849 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1849
Chapter 107 Unrelated Donor Cord Blood Transplantation for Hematologic Malignancies 1645
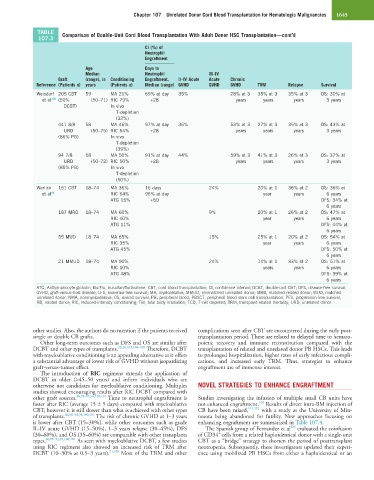
TABLE Comparison of Double-Unit Cord Blood Transplantation With Adult Donor HSC Transplantation—cont’d
107.3
CI (%) of
Neutrophil
Engraftment
Age Days to
Median Neutrophil III–IV
Graft (range), in Conditioning Engraftment, II–IV Acute Acute Chronic
Reference (Patients n) years (Patients n) Median (range) GVHD GVHD GVHD TRM Relapse Survival
Weisdorf 205 CBT 59 MA 21% 69% at day 35% 28% at 3 35% at 3 35% at 3 OS: 30% at
et al 100 (60% (50–71) RIC 79% +28 years years years 3 years
DCBT) In vivo
T-depletion
(32%)
441 8/8 58 MA 46% 97% at day 36% 53% at 3 27% at 3 35% at 3 OS: 43% at
URD (50–75) RIC 54% +28 years years years 3 years
(86% PB) In vivo
T-depletion
(39%)
94 7/8 58 MA 50% 91% at day 44% 59% at 3 41% at 3 26% at 3 OS: 37% at
URD (50–72) RIC 50% +28 years years years 3 years
(85% PB) In vivo
T-depletion
(50%)
Warlick 151 CBT 18–74 MA 36% 16 days 24% 20% at 1 36% at 2 OS: 36% at
et al 94 RIC 64% 96% at day year years 6 years
ATG 15% +50 DFS: 34% at
6 years
187 MRD 18–74 MA 60% 9% 20% at 1 26% at 2 OS: 47% at
RIC 40% year years 6 years
ATG 11% DFS: 44% at
6 years
55 MUD 18–74 MA 65% 15% 25% at 1 20% at 2 OS: 54% at
RIC 35% year years 6 years
ATG 45% DFS: 50% at
6 years
21 MMUD 18–74 MA 90% 24% 14% at 1 33% at 2 OS: 51% at
RIC 10% years years 6 years
ATG 48% DFS: 39% at
6 years
ATG, Antilymphocyte globulin; Bu/Flu, busulfan/fludarabine; CBT, cord blood transplantation; CI, confidence interval; DCBT, double-unit CBT; DFS, disease-free survival;
GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; LFS, leukemia-free survival; MA, myeloablative; MMUD, mismatched unrelated donor; MRD, matched related donor; MUD, matched
unrelated donor; NMA, nonmyeloablative; OS, overall survival; PB, peripheral blood; PBSCT, peripheral blood stem cell transplantation; PFS, progression-free survival;
RD, related donor; RIC, reduced-intensity conditioning; TBI, total body irradiation; TCD, T-cell depleted; TRM, transplant-related mortality; URD, unrelated donor.
other studies. Also, the authors do no mention if the patients received complications seen after CBT are encountered during the early post-
single or double CB grafts. transplantation period. These are related to delayed time to hemato-
Other long-term outcomes such as DFS and OS are similar after poietic recovery and immune reconstitution compared with the
DCBT and other types of transplants. 22,26,102,106–109 Therefore, DCBT transplantation of related and unrelated donor PB HSCs. This leads
with myeloablative conditioning is an appealing alternative as it offers to prolonged hospitalization, higher rates of early infectious compli-
a substantial advantage of lower risk of GVHD without jeopardizing cations, and increased early TRM. Thus, strategies to enhance
graft-versus-tumor effect. engraftment are of immense interest.
The introduction of RIC regimens extends the application of
DCBT in older (>45–50 years) and infirm individuals who are
otherwise not candidates for myeloablative conditioning. Multiples NOVEL STRATEGIES TO ENHANCE ENGRAFTMENT
studies showed encouraging results after RIC DCBT compared with
other graft sources. 86,88–92,94,100,101 Time to neutrophil engraftment is Studies investigating the infusion of multiple small CB units have
110
faster after RIC (average 15 ± 5 days) compared with myeloablative not enhanced engraftment. Results of direct intra-BM injection of
CBT; however it is still slower than what is achieved with other types CB have been mixed, 111,112 with a study at the University of Min-
of transplants. 86,88–92,94,100,101 The risk of chronic GVHD at 1–3 years nesota being abandoned for futility. New approaches focusing on
is lower after CBT (15–30%), while other outcomes such as grade enhancing engraftment are summarized in Table 107.4.
125
II–IV acute GVHD (15–50%), 1–3 years relapse (30–45%), DFS The Spanish group of Fernandez et al evaluated the coinfusion
+
(30–60%), and OS (35–60%) are comparable with other transplants of CD34 cells from a related haploidentical donor with a single-unit
types. 86,88–92,94,100,101 As seen with myeloablative DCBT, a few studies CBT as a “bridge” strategy to shorten the period of posttransplant
using RIC regimens also showed an increased risk of TRM after neutropenia. Subsequently, these investigators updated their experi-
DCBT (10–30% at 0.5–3 years). 91,100 Most of the TRM and other ence using mobilized PB HSCs from either a haploidentical or an