Page 1942 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1942
1722 Part XI Transfusion Medicine
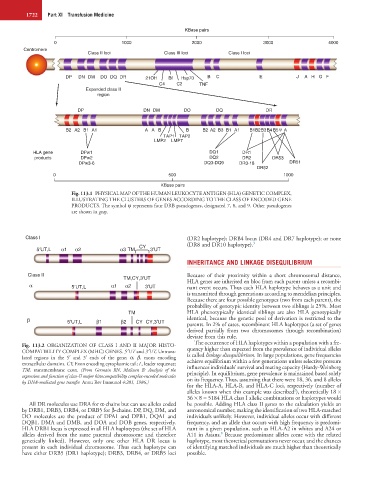
KBase pairs
0 1000 2000 3000 4000
Centromere
Class II loci Class III loci Class I loci
DP DN DM DO DQ DR 21OH Bf Hsp70 B C E J A H G F
C4 C2 TNF
Expanded class II
region
DP DN DM DO DQ DR
B2 A2 B1 A1 A A B B B2 A2 B3 B1 A1 B1 B2B3B4 B5 ψ A
TAP1 TAP2
LMP2 LMP7
HLA gene DPw1 DQ1 DR1
products DPw2 DQ2 DR2 DR53
DPw3-6 DQ3-DQ9 DR3-18 DR51
DR52
0 500 1000
KBase pairs
Fig. 113.1 PHYSICAL MAP OF THE HUMAN LEUKOCYTE ANTIGEN (HLA) GENETIC COMPLEX,
ILLUSTRATING THE CLUSTERS OF GENES ACCORDING TO THE CLASS OF ENCODED GENE
PRODUCTS. The symbol ψ represents four DRB pseudogenes, designated 7, 8, and 9. Other pseudogenes
are shown in gray.
Class I (DR2 haplotype); DRB4 locus (DR4 and DR7 haplotype); or none
CY (DR8 and DR10 haplotype). 3
5′UT,L α1 α2 α3 TM 3′UT
INHERITANCE AND LINKAGE DISEQUILIBRIUM
Class II Because of their proximity within a short chromosomal distance,
TM,CY,3′UT HLA genes are inherited en bloc from each parent unless a recombi-
α 5′UT,L α1 α2 3′UT nant event occurs. Thus each HLA haplotype behaves as a unit and
is transmitted through generations according to mendelian principles.
Because there are four possible genotypes (two from each parent), the
probability of genotypic identity between two siblings is 25%. Most
TM HLA phenotypically identical siblings are also HLA genotypically
β 5′UT,L β1 β2 CY CY,3′UT identical, because the genetic pool of derivation is restricted to the
parents. In 2% of cases, recombinant HLA haplotypes (a set of genes
derived partially from two chromosomes through recombination)
deviate from this rule.
The occurrence of HLA haplotypes within a population with a fre-
Fig. 113.2 ORGANIZATION OF CLASS I AND II MAJOR HISTO- quency higher than expected from the prevalence of individual alleles
COMPATIBILITY COMPLEX (MHC) GENES. 5′UT and 3′UT, Untrans- is called linkage disequilibrium. In large populations, gene frequencies
lated regions in the 5′ and 3′ ends of the gene; α, β, exons encoding achieve equilibrium within a few generations unless selective pressure
extracellular domains. CY, Exon encoding cytoplasmic tail; L, leader sequence; influences individuals’ survival and mating capacity (Hardy-Weinberg
TM, transmembrane exon. (From Germain RN, Malissen B: Analysis of the principle). In equilibrium, gene prevalence is maintained based solely
expression and function of class-II major histocompatibility complex-encoded molecules on its frequency. Thus, assuming that there were 18, 36, and 8 alleles
by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Annu Rev Immunol 4:281, 1986.)
for the HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C loci, respectively (number of
2
alleles known when this example was described ), theoretically 18 ×
36 × 8 = 5184 HLA class I allelic combinations or haplotypes would
All DR molecules use DRA for α-chains but can use alleles coded be possible. Adding HLA class II genes to the calculation yields an
by DRB1, DRB3, DRB4, or DRB5 for β-chains. DP, DQ, DM, and astronomical number, making the identification of two HLA-matched
DO molecules are the product of DPA1 and DPB1, DQA1 and individuals unlikely. However, individual alleles occur with different
DQB1, DMA and DMB, and DOA and DOB genes, respectively. frequency, and an allele that occurs with high frequency is predomi-
HLA DRB1 locus is expressed in all HLA haplotypes (the set of HLA nant in a given population, such as HLA-A2 in whites and A24 or
8
alleles derived from the same parental chromosome and therefore A11 in Asians. Because predominant alleles come with the related
genetically linked). However, only one other HLA DR locus is haplotype, most theoretical permutations never occur, and the chances
present in each individual chromosome. Thus each haplotype can of identifying matched individuals are much higher than theoretically
have either DRB5 (DR1 haplotype); DRB3, DRB4, or DRB5 loci possible.