Page 1986 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1986
1760 Part XI Transfusion Medicine
Frozen human plasma
Thaw at 4°C
Cryoprecipitate Cryosupernatant
FVIII/vWF FIX complex Optional
Fibrinogen adsorption
Factor XIII Antithrombin steps
8% Ethanol, pH 7.2
Fraction I Fraction I
precipitate supernatant
Antithrombin
Fibrinogen
25% Ethanol, pH 6.8
Fraction II + III Fraction II + III
precipitate supernatant
Immune
globulins
18% Ethanol, pH 5.2
Fraction IV-1 Fraction IV-1
precipitate supernatant
FIX complex
API, AT
40% Ethanol, pH 5.8
Fraction IV-4 Fraction IV-4
precipitate supernatant
PPF with
Fraction V
40% Ethanol, pH 4.8
Fraction V Fraction V
precipitate supernatant
Albumin
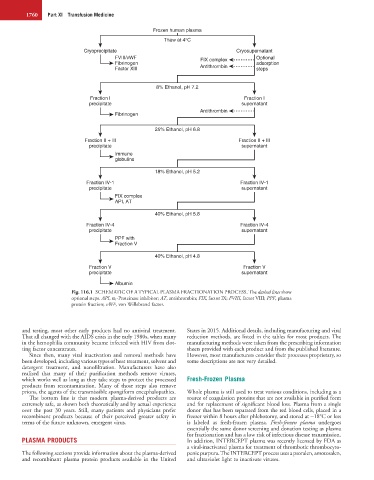
Fig. 116.1 SCHEMATIC OF A TYPICAL PLASMA FRACTIONATION PROCESS. The dashed lines show
optional steps. API, α 1-Proteinase inhibitor; AT, antithrombin; FIX, factor IX; FVIII, factor VIII; PPF, plasma
protein fraction; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
and testing, most other early products had no antiviral treatment. States in 2015. Additional details, including manufacturing and viral
That all changed with the AIDS crisis in the early 1980s, when many reduction methods, are listed in the tables for most products. The
in the hemophilia community became infected with HIV from clot- manufacturing methods were taken from the prescribing information
ting factor concentrates. sheets provided with each product and from the published literature.
Since then, many viral inactivation and removal methods have However, most manufacturers consider their processes proprietary, so
been developed, including various types of heat treatment, solvent and some descriptions are not very detailed.
detergent treatment, and nanofiltration. Manufacturers have also
realized that many of their purification methods remove viruses,
which works well as long as they take steps to protect the processed Fresh-Frozen Plasma
products from recontamination. Many of those steps also remove
prions, the agents of the transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Whole plasma is still used to treat various conditions, including as a
The bottom line is that modern plasma-derived products are source of coagulation proteins that are not available in purified form
extremely safe, as shown both theoretically and by actual experience and for replacement of significant blood loss. Plasma from a single
over the past 30 years. Still, many patients and physicians prefer donor that has been separated from the red blood cells, placed in a
recombinant products because of their perceived greater safety in freezer within 8 hours after phlebotomy, and stored at −18°C or less
terms of the future unknown, emergent virus. is labeled as fresh-frozen plasma. Fresh-frozen plasma undergoes
essentially the same donor screening and donation testing as plasma
for fractionation and has a low risk of infectious disease transmission.
PLASMA PRODUCTS In addition, INTERCEPT plasma was recently licensed by FDA as
a viral-inactivated plasma for treatment of thrombotic thrombocyto-
The following sections provide information about the plasma-derived penic purpura. The INTERCEPT process uses a psoralen, amotosalen,
and recombinant plasma protein products available in the United and ultraviolet light to inactivate viruses.